* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AnS 214 SI Session 5 Sunday, September 13, 8pm A) Antigens and
Survey
Document related concepts
Duffy antigen system wikipedia , lookup
Immunocontraception wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Complement system wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
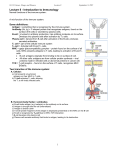
AnS 214 SI Session 5 Sunday, September 13, 8pm A) Antigens and receptors 1) Compare and contrast MHC-I and MHC-II proteins according to the following parameters: On what cell types are they found? What kinds of antigens do they exhibit (where do the antigens come from)? What cell types can adhere to these receptors? 2) What is a hapten, and how does it differ from 'regular' antigens? Give examples of common haptens. 3) What is an epitope? B) T-cell activation 1) In the space below, list the stages of T-cell activation (clonal selection, antigen recognition, lethal hit, costimulation) in order, provide a brief description of the stage and draw a continuous diagram representing the events visually. 1.______________________ 2.______________________ 3.______________________ 4.______________________ 2) After activation, T-helper cells secrete interleukins that activate other areas of the immune system. Explain how T-helper interleukins function in the following areas. Non-specific defense: Humoral Immunity: Cellular immunity: 3) T helper cells are alternatively called ____________ and cytotoxic T cells are called ____________. C. B cell activation. 1) In the space below, list the stages of B-cell activation (clonal selection, antigen recognition, attack, antigen presentation, differentiation) in order, provide a brief description of the stage and draw a continuous diagram representing the events visually. 1._________________ 2._________________ 3._________________ 4._________________ 5._________________ 2) T/F Plasma cells are exceptionally long-lived cells, covered in antibodies, which they then release to combat pathogens. If you put False, justify your answer by changing the sentence to make it true. 3) What are the three organelles necessary for the extreme rates of protein synthesis found in plasma cells? 4) Write in the names of the antibody killing mechanism corresponding to the description. _________________ Antibody binds to multiple enemy cells, immobilizing them. _________________ Antibody creates antigen-antibody complex that is too heavy to remain soluble in plasma, making it vulnerable to phagocytosis by eosinophils. _________________ IgM or IgG change shape upon binding to antigen and activate a reaction cascade which initializes inflammation, immune clearance, phagocytosis, cytolysis. _________________ Antibodies coat pathogen surface, rendering pathogenic site inactive. D. Memory 1) What is the origin of Tm cells and how do they aid immune memory? 2) How do memory B cells contribute to immune memory? 3) Fill in the diagram at right with axis labels and IgG titer data line, and use it to explain the advantages of secondary response (why is there no illness)? E. Complement fixation. Fill in the blanks, describing steps involved with complement fixation.