* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Kingdom Animalia
Survey
Document related concepts
Embryonic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Cambrian explosion wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Chimera (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Regeneration in humans wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
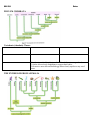
SBI 3U Date: Kingdom Animalia Many people have trouble understanding the leap from our protist ancestor around 700 mya to animals. -Feeding cells indented to form a hollow cavity Protist Ancestor -Colonial -Flagellated - Some cells specialized for feeding -Indented cell forms an early digestive cavity allowing organism to capture and digest food. The Simplest Phyla: Porifera: The Sponges Sponges have very similar structures to ancestral protists. They contain an outer layer of _________________ that create a continuous current of water that passes through pores into the body. Food particles entering with water are captured by specialized cells called ______________. Water is forced out the ______________which is a simple opening at the top of the sponge. Porifera is the most distantly related of all animals Asymmetrical Cnidaria: The Jellyfish, Coral, Hydras & Anemones Cnidarians are the simplest animals that have specialized ________________, _____________________, _____________________ and _______________________ tissues. All cnidarians have tentacles with stinging cells called ________________ which contain a barbed tube that delivers a paralyzing sting to prey and attackers. Radial Symmetry The Protostome Phyla: (in embryonic development, the mouth forms before the anus) Phyla Arthropoda Nematoda Annelida Mollusca Rotifera Platyhelminthes Examples Spiders, mites, scorpions, lobsters Heartworm, pinworms Earthworms Snails, clams, octopus, squid Rotifers Tapeworms, liver flukes Key Features SBI 3U Date: The protostomes are extremely diverse. Just within phylum arthropoda, class Inescta, there are over 1.1 million described species! ALL PROTOSTOMES HAVE: The Deuterostome Phyla: (during embryonic development, the anus forms before the mouth) The Echinoderms: The only phylum that are invertebrates (no rigid backbone structure) Though visibly different, echinoderms have a complete digestive system, nervous system and a simple circulatory system. The Chordates: the most complex living organisms that all have a notochord (primitive backbone) or segmented vertebrae and bilateral symmetry. Interesting enough, the embryonic development of these advanced organisms have striking similarities to their more primitive cousins. Observing embryology is like watching evolution ! SIMILARITIES Day 1: Day 2- 4: Day 5-7: Day 9-12: Day 18-23: SBI 3U Date: PHYLUM CHORDATA Vertebrate (chordate) Classes Vertebrates evolved key features that allowed them to conquer land: 1) Limbs allowed early amphibians to support their bodies 2) Protective outer skin and shelled eggs allowed early reptiles to stay out of water THE ENTIRE KINGDOM ANIMALIA SBI 3U Date: