* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Atomic Structure
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
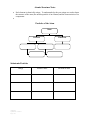
Atomic Structure Notes Each element is chemically unique. To understand why they are unique we need to know the structure of the atom (the smallest particle of an element) and the characteristics of its components. Particles of the Atom Atom Nucleus Electrons Subatomic Particles Charge Electron Proton Neutron 148093109 Updated On: 6/26/2017 Page 1 of 3 Relative mass Location in atom Atomic Structure Nucleus •In the center of the atom and contains the _______________ and __________________ •Makes up ____________of the mass of the atom. Periodic Table Representation of an Element 6 C Carbon 12.001 •Atomic number = ______________________ •Number of protons = ____________________________________________________ •Mass number = _____________________________________ (total particles in nucleus) •_________________________ is the average mass of all known isotopes of the element –Most abundant isotope can be found by rounding atomic mass to nearest whole number Comparing Atoms •Same element always has the _____________________________________. –Ex: Carbon always has 6 protons no matter what. •Isotope is the same element with different number of ________________________ therefore, the mass number will be different for the same element. All atoms of an element are considered an isotope, some are more common than others. •Ion is same element with a different number of __________________. An ion is a charged atom. –Cation is a positive ion –Anion is an negative ion 148093109 Updated On: 6/26/2017 Page 2 of 3 Isotopes •All atoms of an element are considered an isotope, only some are more common than others. •Atomic mass is the ______________________ of all isotopes of the element. •Even though isotopes have different amounts of neutrons they are still chemically alike since they have the same number of protons and electrons. •To find the most common isotope round the atomic mass to nearest whole number. -Ex: Carbon-12 is the most common isotope of carbon Which isotope is the most common for the element Boron? Isotopes of Carbon •Isotopic notation: Carbon-12 C •Isotopic notation: Carbon-14 C Why is Carbon-14 in Red? •Carbon-14 is an unstable isotope and decays as time goes on. That’s why caron-14 is used to date objects. •Unstable isotopes called radioisotopes undergo changes and release energy to become more stable. These isotopes have many uses which we will discuss in the Nuclear Chemistry section of our class. Now, let’s compare the three isotopes of Lithium! How many protons does Lithium-6 have? ________ How many protons does Lithium-7 have? ________ How many protons does Lithium-8 have? ________ How many neutrons does Lithium-6 have? ________ How many neutrons does Lithium-7 have? ________ How many neutrons does Lithium-8 have? ________ How many electrons does Lithium-6 have? ________ How many electrons does Lithium-7 have? ________ How many electrons does Lithium-8 have? ________ 148093109 Updated On: 6/26/2017 Page 3 of 3