* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Effects of War
Texas in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Lewis's Farm wikipedia , lookup
Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
Anaconda Plan wikipedia , lookup
Origins of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Secession in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Baltimore riot of 1861 wikipedia , lookup
Economy of the Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Pillow wikipedia , lookup
Conclusion of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
Carpetbagger wikipedia , lookup
Capture of New Orleans wikipedia , lookup
Lost Cause of the Confederacy wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Reconstruction era wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Radical Republican wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
South Carolina in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Jubal Early wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Mississippi in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
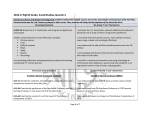
Effects of War Battles with Political Significances Economic & Political Impact of the War Individual Leaders Impact of Reconstruction • Long and costly/ destructive The possibility of foreign governments support for the Confederacy led to Lincoln issuing the Emancipation Proclamation. The Civil War had a significant impact on the economies of both the Union and the Confederacy. The North’s industry generally improved, and US government policies moved to favor business and expansion. The South’s economy was ruined by the Civil War. The Confederacy possessed superior military leadership. The severity of Reconstruction resulted in Southern resentment and distrust of the North, which continued for a long time. The defeat of the Confederacy preserved the Union and ended slavery in the South. Abraham Lincoln • Northern victory • Restoration of the Union • Emancipation of the slaves Emancipation Proclamation — (may be seen as a foreign policy strategy - issued after the Battle of Antietam ) • Freed those slaves located in "rebelling" states • Made the destruction of slavery a Northern war aim • Discouraged any interference of foreign governments The Battles of Antietam and Gettysburg were turning points in the war and the Gettysburg Address described the war as a struggle to preserve a nation dedicated to the proposition that "all men are created equal" and "government of the people, by the people, and for the people." Lincoln and Lee were men of integrity whose views of the nature of the United States were different, leading to an unavoidable conflict. Lincoln’s Plan Economy of the North • Economic prosperity and westward expansion • Federal subsidies of railroads • Homestead Act — (1862) gave free public land in the western territories to settlers who would live on and farm the land • President of the Union; determined to preserve the Union, by force if necessary • The assassination of Lincoln just after Lee’s surrender enabled Radical Republicans to influence the more punitive manner Reconstruction plans were implemented Economy of the South • Economic distress Robert E. Lee • Loss of land and revenue • Confederate General of the Army of Northern Virginia (Lee opposed secession, but did not believe the Union should be held together by force), who urged Southerners to accept defeat and unite as Americans again, when some Southerners wanted to fight on after Appomattox — site of Lee’s surrender to Grant • Generations of poor farmers Politics of the North • The Emancipation Proclamation and the role of the Radical Republicans • Federal powers increased Politics of the South • Strong national government necessary despite the creation of a confederacy Frederick Douglass • Former slave; prominent black abolitionist; who urged Lincoln to recruit former slaves to fight in the Union army • States’ rights defenders found a home in the Democratic Party, which dominated the South for the next century Battles with Political Economic & Political Impact • Secession was illegal. Since Southern states had not left the Union, legitimate state governments loyal to the Union could be restored to the Union. • To reunify, the federal government should not punish the South, but act "with malice towards none, with charity for all… to bind up the nation’s wounds…" Ulysses Grant • Union military commander, who won victories over the South after several Union commanders had failed • Few industries Effects of War The economic and political gains of former slaves in the South were temporary. Individual Leaders Radical Republican Plan • Punitive towards former Confederate States — not allowed back into the Union immediately, but were put under military occupation • Believed in aggressively guaranteeing voting and other civil rights to African Americans. • Clashed often with Andrew Johnson Andrew Johnson’s Plan • Continued the plan of Lincoln allowing Confederate state to be readmitted to the union if they would declare secession illegal, swear allegiance the Union and ratify the 13th Amendment • Support of states’ rights angered Radicals because they felt his plan did not address the needs of former slaves (land, voting rights, & protection under the law) — resulted in impeachment Impact of Reconstruction Significances of the War Women Civil War Amendments • Elizabeth Cady Stanton and Susan B. Anthony • 13th — abolished slavery • Seneca Falls Declaration — women’s suffrage • Worked for equal rights for women before and after the war • 14th - prohibited the denial of equal rights under the law to any American • 15th — voting rights were guaranteed regardless of "race, color, or previous condition of servitude" (slavery) Long Term Impact of Reconstruction • Southern states were embittered and devastated • Southern farms, factories, and railroads were destroyed • Richmond and Atlanta were in ruins • The South remained backward, agricultural and poor • The North and the Midwest became strong and industrial laying the foundation for industrialization and becoming a global economic power End of Reconstruction • The close election of 1876 resulted in the Compromise of 1877 • Southern Democrats supported the electoral college vote and the Republicans agreed to end military occupation • Former Confederates, who controlled the Democratic Party in the south, regained power and the "Jim Crow Era" began