* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Endocrine System
Survey
Document related concepts
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Metabolic syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis wikipedia , lookup
Growth hormone therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hypoglycemia wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
Insulin resistance wikipedia , lookup
Diabetes mellitus type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Diabetes management wikipedia , lookup
Gestational diabetes wikipedia , lookup
Complications of diabetes mellitus wikipedia , lookup
Diabetic ketoacidosis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
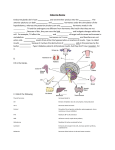
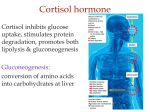
Endocrine System The endocrine system is a complex network of glandular tissues that secrete hormones directly into the blood which are used by "target" organs. The endocrine system controls a variety of important functions such as energy metabolism, reproduction, and stress response. The pituitary gland is often referred to as the "master gland" because it regulates the hormones used by the thyroid, adrenal cortex, ovaries, testes, and the breasts (in women). The pituitary is located in the brain below the hypothalamus. It peaks in size in middle age and then gradually shrinks. Pancreas Insulin Response The pancreas secretes insulin, a hormone which is critical to the metabolism of glucose (blood sugar). Insulin continues to be produced in sufficient quantities in older adults but their muscle cells may become less sensitive to the effects of insulin (probably due to a loss in the number of insulin receptor sites in the cell wall). After age 50, the "normal" fasting glucose level rises 6 to 14 milligrams per deciliter every 10 years. Adult onset diabetes or Type II diabetes occurs when the body develops resistance to insulin. It is usually managed through diet, exercise, and oral hypoglycemic medications. Sometimes people stop producing insulin and then insulin injections are needed. A number of studies indicate that adult onset diabetes is related to obesity and inactivity. Adrenal Glands The adrenals are located just above the kidney's and secrete several hormones including aldosterone and cortisol. aldosterone is important in regulating fluid and electrolyte balance. On average, aldosterone levels are 30% lower in adults age 70 to 80 years old than in younger adults. Lower aldosterone levels may cause orthostatic hypotension (a drop in blood pressure with changes in position). cortisol is a stress response hormone that has anti-inflammatory and anti-allergy effects. Secretion of cortisol diminishes by 25% with age although the significance of this remains unclear. DHEA blood levels decline with age. However, the functional consequences of this decline are not clear. If this site is still available, it can be found at http://www.ageworks.com/information_on_aging/changeswithaging/