* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Endocrine System Notes
Survey
Document related concepts
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
History of catecholamine research wikipedia , lookup
Neuroendocrine tumor wikipedia , lookup
Cryptorchidism wikipedia , lookup
Menstrual cycle wikipedia , lookup
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (female-to-male) wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (menopause) wikipedia , lookup
Bioidentical hormone replacement therapy wikipedia , lookup
Endocrine disruptor wikipedia , lookup
Xenoestrogen wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Mammary gland wikipedia , lookup
Breast development wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
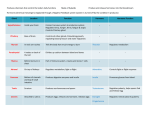
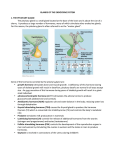
The Endocrine System I. II. Endocrine Glands A. “Ductless” Glands B. Pass their secretions directly into the bloodstream Hormones A. “Chemical Messengers” B. Regulate chemical reactions in the body, bodily functions III. Thyroid Gland A. Located at the base of the neck, just below Larynx B. Hormone – Thyroxin C. Controls metabolism D. Too little thyroxin may lead to sluggishness, weight gain E. Too much thyroxin may lead to hyperactivity, increased appetite, no weight gain IV. Parathyroid Gland A. Four small pea-shaped glands on the backside of the Thyroid B. Hormone – parahormone specific to the balance of calcium V. VI. VII. Adrenal Glands A. Located on top of the kidneys B. Hormone – Adrenaline C. “glands of combat” - fight or flight response D. Controls body’s reaction to stress – increase sugar levels/energy E. Also controls levels of salt and water in the body Islets of Langerhans A. Located throughout the Pancreas B. Hormone – Insulin C. Regulates amount of glucose (sugar) in the blood D. If gland does not operate correctly - Diabetes Thymus Gland A. Located behind top of sternum (breast bone) B. Hormones – Thymosin, Thymopoietin C. Important in the normal development of the immune response D. Large in infants and children; begins to shrink by adolescence and adulthood. VIII. Ovaries – Female only – inactive until Puberty A. Two glands in pelvic region B. Hormones - Estrogen, Progesterone C. Primary function as an organ to store ovum D. Estrogen controls female characteristics – development of breasts, widening of pelvic bones, menstruation E. Progesterone secreted during pregnancy IX. Testicles/Testes – Male only – inactive until Puberty A. Two glands in scrotum B. Hormone – Testosterone C. Primary function as an organ to produce sperm D. Testosterone controls male characteristics – growth of body hair, widening of shoulders, muscle development, enlargement of larynx (Adam’s Apple) and deepening of voice X. Pineal Gland A. Located in the brain B. Hormone - Melatonin C. Regulates sleep, hibernation (animals), aging – “sociological” or “biological clock” XI. XII. Hypothalamus A. Located in the brain B. Controls many bodily functions including the release of hormones from the pituitary gland C. Regulates body temperature, thirst, and hunger D. Site of emotions and the effect emotions can have on the body Pituitary Gland A. Located at the base of the brain B. Hormone – Human Growth Hormone (HGH) C. Regulates body’s growth and development D. Also produces several other hormones E. Referred to as the “Master Gland” – controls the functioning of many other glands/organs – thyroid, adrenal, kidney