* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Name Period ______ Due Date Review Stations Key Station 1
Survey
Document related concepts
Ionizing radiation wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear fusion wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear fission product wikipedia , lookup
Technetium-99m wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear fission wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Inertial electrostatic confinement wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear fusion–fission hybrid wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear binding energy wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear transmutation wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
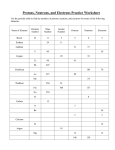
Unit 4: Splitting & Unstable Matter: Atoms & Nuclear Chemistry Name ________________________________________ Period ________ Due Date ______________________ Review Stations Key Station 1: Parts of an Atom PART I: Model of an Atom Key: = protons = neutrons = electrons PART II: Questions 1. Protons and neutrons 2. C 3. A Nucleus 4. + 5. – 6. An electron has a much smaller mass (1/1836 the mass of a proton or neutron) than a proton or neutron. 7. Protons and electrons Station 2: Calculating Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons Complete the following table. Description Hyphen Notation Nuclear Symbol An atom with a mass of 65 and an Copper-65 atomic number of 29 An isotope with 33 protons, 42 neutrons, and 33 electrons An atom that contains 64 neutrons and has a mass of 113 amu An atom with a nucleus that contains 80 protons and 118 neutrons An isotope that is made up of 51 electrons and 51 protons An atom that has 72 neutrons and 50 electrons Arsenic-75 75 Indium-113 113 49In 33As Mercury-198 Antimony-121 121 51Sb Tin-122 122 50Sn Hyphen Notation Bohr Model Nuclear Symbol Lithium-6 6 3Li Helium-4 4 2He 7 3Li 23 11Na Station 3: Isotopes 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. B C A B The isotope shown above has 16 protons,16 electrons, 18 neutrons, and a mass number of 34. I and III &II and IV Station 4: Average Atomic Mass 10.811 amu 28.088 amu 79.90 amu a. 35.45 amu b. Chlorine (Cl) Potassium-39 because the average atomic mass is closer to 39 than 41. Station 5: Radioactive Particles Alpha Beta Gamma 2+ Charge 1- Charge No charge Helium Nucleus Electron Electromagnetic Radiation 4 amu 0.0055 amu 0 amu Stopped by paper, wood, cloth, etc. Stopped by aluminum or other metals Stopped by lead Least dangerous to humans Most dangerous to humans alpha beta gamma 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. A A C B B D Station 6: Balancing Nuclear Equations Balancing Nuclear Equations Answer Key 233U229Th 4 He 1) 92 90 2 2) 14C14 N 0e 6 7 1 16 N 0 e16O 3) 7 -1 8 192Pt 4 He188Os 4) 78 2 76 32P 0 e32S 5) 15 - 1 16 226 Ra4 He222Rn 0 6) 88 2 86 0 Station 7: Fusion vs. Fission 1. C 2. C 3. C 4. B 5. A 6. a. Fission b. Fusion Station 8: Half-Life 1. c 2. a If the isotope had a long half-life, it would stay in your body causing radiation poisoning or cancer. 3. Long half-lives because takes more time to decay. 4. a. 200 years b. 17 grams c. 150 years