* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 7 Heredity: Chp 11 Non-Mendelian Genetics Notes
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Selective breeding wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
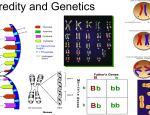
NON-MENDELIAN GENETICS Simple Mendelian Inheritance = controlled by dominant and recessive paired alleles. Many inheritance patterns are more complicated than those in Pea plants. INCOMPLETE DOMINANCE Appearance of a 3rd phenotype Complete Dominance = TT, Tt same phenotype Incomplete Dominance = intermediate phenotype for Tt Red flower and White flower F1 all pink = Rr Neither allele is COMPLETELY dominant Combine to give a new trait Rr x Rr 1:2:1 RR = Red Rr = Pink rr = White CODOMINANCE Expressed both alleles Black x White feathered birds B and W (both capital) They would be Black if Mendel’s worked They would be Gray if Incomplete dominance Heterozygous have some black and some white feathers MULTIPLE PHENOTYPES FROM MULTIPLE ALLELES More than 2 alleles control a trait in a population 4 alleles for a single gene in Rabbit color Each rabbit only has 2 of the 4 SEX DETERMINATION Human = 23n 46 = 2n 22 pairs of matching homologous chromosomes called = Autosomes Look exactly alike 23rd pair differs in Male and Female = Sex Chromosomes Female = XX (1 kind of Gamete) Male = XY (2 kinds of Gametes) A punnett square shows a 50/50% chance of either sex ENVIRONMENTAL INFLUENCES When you solve puzzle of dominant and recessive and understand other patterns of heredity = still not complete As organisms develop, many factors can influence how the gene is expressed Internal Environment - Age or Gender can affect gene function Color of feathers in birds = male breeding plumage Horns on Buck deer Controlled by different hormones These hormones are controlled by different sets of genes External Environment - Temperature, nutrition, light, chemical and infectious agents influence gene expression Temp has affect of color in Rabbit coats Bacteria color Fig 14.9 Light affects leaf size and shape APPLIED GENETICS DETERMINING GENOTYPES Recessive traits = Homozygous recessive Same phenotype = TT, Tt Testcross = cross individual unknown genotype with an individual of known genotype Test organism = usually homozygous recessive for trait SELECTIVE BREEDING Selective Breeding = breed domesticated animals and plants for desired traits Cattle, Fruit, Vegetables “True Breed” Don’t want a heterozygous if it is a weak gene Pedigree = graphic representation of an individual’s family tree (patterns of inheritance) Poor hips in a Lab = don’t breed TT x TT tt x tt Hybid = cross two types of fish - one might be disease resistant - Bass = Florida stain is bigger Cattle not resistant to heat but good meat Cross with cattle resistant = Hybrid Takes a while to get a “pure bred” hybrid