* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide ()
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Bird vocalization wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Apical dendrite wikipedia , lookup
Neural oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Mirror neuron wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Anatomy of the cerebellum wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Muscle memory wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Pre-Bötzinger complex wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
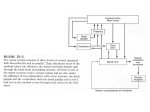
The corticospinal and bulbospinal upper motor neuron pathways. Upper motor neurons have their cell bodies in layer V of the primary motor cortex (the precentral gyrus, or Brodmann’s area 4) and in the premotor and supplemental motor cortex (area 6). The upper motor neurons in the primary motor cortex are somatotopically organized (right side of figure). Axons of the upper motor neurons descend through the subcortical white matter and the posterior limb of the internal capsule. Axons of the pyramidal or corticospinal system descend through the brainstem in the cerebral peduncle of the midbrain, the basis pontis, and the medullary pyramids. At the cervicomedullary junction, most Causes corticospinal axons decussate into Harrison's the contralateral corticospinal tract of the lateral spinal cord, but 10–30% remain Source: Neurologic of Weakness and Paralysis, Principles of Internal Medicine, 19e ipsilateral in the anterior spinal cord. Corticospinal neurons synapse on premotor interneurons, but some—especially in the cervical enlargement and Citation: Kasper D, Fauci A, Hauser S, Longo D, Jameson J, Loscalzo J. Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine, 19e; 2015 Available at: those connecting with motor neurons to distal limb muscles—make direct monosynaptic connections with lower motor neurons. They innervate most http://mhmedical.com/ Accessed: April 29, 2017 densely the lower motor neurons of hand muscles and are involved in the execution of learned, fine movements. Corticobulbar neurons are similar to Copyright © 2017 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved corticospinal neurons but innervate brainstem motor nuclei.