* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download L4_bacterial metabolism7e
Metabolic network modelling wikipedia , lookup
Enzyme inhibitor wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical cascade wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
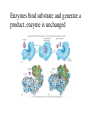
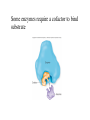
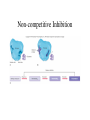
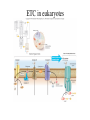
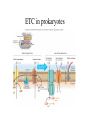
Metabolism • The sum total of ALL chemical reactions within a cell – Catabolic – Anabolic Energy is the capacity to do work • Potential energy: stored energy • Kinetic energy: energy of motion Organisms obtain energy from different sources • Photosynthetic organisms obtain energy from… • Chemoorganotrophs obtain energy from….. Chemoorganotrophs depend on photosynthetic organisms Let’s focus on metabolism of chemoorganotrophs (bacteria) • Where do they obtain carbon? • How do they generate energy? What promotes chemical reactions in biological systems? What promotes chemical reactions in biological systems? ENZYMES Enzymes bind substrate and generate a product, enzyme is unchanged Some enzymes require a cofactor to bind substrate Coenzymes carry electrons How does this relate to metabolism? Factors that influence an enzyme: Temperature • What happens as temperature increases? • What is the optimum temperature? Factors that influence an enzyme: pH • What pH do most enzymes function optimally? Enzyme inhibitors • Inhibit the binding of the substrate to the active site – Competitive inhibition – Non-Competitive Inhibition Competitive Inhibition Non-competitive Inhibition Oxidation/reduction reactions Biological Oxidation ATP is made in catabolic reactions and used in anabolic reactions Ways cells make ATP • Substrate level phosphorylation • Oxidative phosphorylation • Photophosphorylation Types of Bacterial Metabolism • Fermentation • Respiration – Aerobic Respiration – Anaerobic Respiration • Photosynthesis Keep in mind…glucose becomes many different things Fermentation • The incomplete breakdown of glucose with an organic compound serving as the final electron acceptor • Only pathway operating is glycolysis Fermentation Lactic Acid Bacteria Saccharomyces produces ethanol Fermentation products can vary Aerobic Respiration • The COMPLETE breakdown of glucose to CO2 and H2O with an inorganic compound serving as the final electron acceptor Remember the pathways in aerobic respiration are… • Glycolysis – Some use Pentose Phosphate Pathway instead • TCA cycle • Electron transport chain What is made as a result of the TCA cycle? • ATP • Reducing power • Precursor metabolites made from alphaketoglutarate and oxaloacetate Electron Transport Chain • Found in the cytoplasmic membrane • Contains electron carriers – – – – Flavoproteins Iron-sulfur proteins Quinones Cytochromes Model for energy release in ETC ETC in eukaryotes ETC in prokaryotes ATP yield from aerobic respiration Comparison of three types of metabolism Remember we are focusing on catabolic reactions • Generate ATP for later use by cell • Generate precursors for other pathways • Need to re-oxidize coenzymes for continual use Precursor metabolites