* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PSYCHONEUROIMMUNOLOGY
Behçet's disease wikipedia , lookup
Complement system wikipedia , lookup
Vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Human leukocyte antigen wikipedia , lookup
Social immunity wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Autoimmune encephalitis wikipedia , lookup
Sociality and disease transmission wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Myasthenia gravis wikipedia , lookup
Pathophysiology of multiple sclerosis wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Immunocontraception wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Gluten immunochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
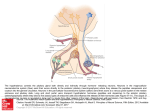
PSYCHONEUROIMMUNOLOGY THE MIND-BODY CONNECTION Breaking down the word: • psycho—emotional behavior • neuro—hypothalamic/pituitary axis • immuno—immune system involvement • -logy—study of Anecdotal evidence of a brain-body connection: • Sara • shaman • placebo Review of electrochemical neurotransmission role of neurotransmitters putative neurotransmitters peptides Peptides is a “buzz” word for understanding psychoneuroimmunology (PNI) “PSYCHO” PART • higher cortical centers communicate with the emotional brain via the limbic system • Papez Circuit (1937)—anatomical substrate for emotion “NEURO” PART • primary function of the hypothalamus is to control the pituitary • this occurs in two ways—direct (posterior pituitary) and indirect (anterior pituitary) Direct control occurs in the posterior pituitary via oxytocin (OXY) and arginine vasopressin (AVP) both are chains of amino acids also called peptides Indirect control occurs in the anterior pituitary—messages stop at the median eminence and release releasing factors examples: GH and GHRH; FSH and FSHRH; they are also peptides (hormones in body) “IMMUNO” PART immune system (IS) • one function of IS is recognition of self v non-self • another function is maintenance of homeostasis—a delicate balance that is interrupted infrequently, but results in pathology when it is Work of IS is carried out by T-cells and Bcells T-cells (thymus) eliminate antigens by attacking them directly or by initiating a cascade of events that results in the release of lymphokines—”natural drug” of IS: structurally a peptide product of T-cells B-cells (bursa of Fabricius) secrete antibodies that search out antigens and combine with them to form immunoglobulins IMMUNE SYSTEM AND STRESS (DISEASE) • 200 A.D.—Galen notes that melancholy women (yellow bile) were more likely to develop cancer than sanguine women (blood) • 1920s—Cannon introduced fight or flight— nervous system arousal to stressful stimuli • 1980s—Norman Cousins, an editor of a large east coast newspaper and astute lay person self-prescribed comedy films for reducing his own recovery time—Marx Brothers, Three Stooges, Candid Camera IMMUNE SYSTEM AND CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM • Direct innervation of IS by CNS bone marrow innervated by vagus nerve (X) CNS structures project fibers to the thymus spleen is innervated by CNS fibers • Various peptides are found in gut tissue where immune actions may be initiated • IS peptides affect thymocyte production and lymphocytes • Weiderman (1987) proposed that peptides act as a “transducer” between experience and disease and hypothesized that every peptide found in the CNS will eventually be shown to have a peripheral role as well • Candace Pert suggested that peptides play a significant role in the holistic approach to mind-disease paradigm • Role of alternative medicines • What do you think now? – about Sara – about shaman – about the placebo effect