* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Electric Field
Electrostatic generator wikipedia , lookup
Hall effect wikipedia , lookup
Insulator (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Eddy current wikipedia , lookup
Multiferroics wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Faraday paradox wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
History of electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Electroactive polymers wikipedia , lookup
Electrocommunication wikipedia , lookup
Static electricity wikipedia , lookup
Electrical injury wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Electromotive force wikipedia , lookup
General Electric wikipedia , lookup
Electric current wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
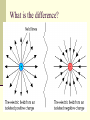
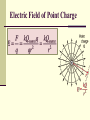
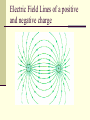
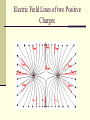
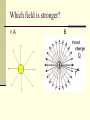
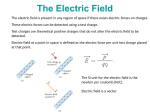
Do Now (9/13/13): 1. How does the electric force change when distance is increased? 2. How does the electric force change when either or both of the charges are increased? Electric Field Physics II Analogy The electric field is the space around an electrical charge just like a gravitational field is the space around a mass. Electric Field Space around a charge. What is the difference? Van de Graaff Generator Builds up static electric charges. Electric field Any charge placed in an electric field will experience a electrical force. The field strength is the electric force per unit charge on any “test charge” placed in the field: E = F /q. E: vector that points in the direction of the net electric force on a positive charge; its units are N / C. F : vector force on the test charge q : test charge, a scalar. Electric Field Vector, E E = F/ qo qo , positive test charge E: electric field strength (vector quantity) Unit: N/C E is analogous to the gravitational field, g, where g=F/m Example 1 A charge of 3µC is used to test the electric field of a central charge of 6C that causes a force of 800N. What is the magnitude of the electric field? Answer: 2.7 x108 N/C Electric Field http://higheredbcs.wiley.com/legacy/colleg e/halliday/0471320005/simulations6e/inde x.htm?newwindow=true Electric Field of Point Charge Practice: Use the rest of class to work on your homework Do Now (9/16/13): A charge of 9µC is used to test the electric field created by a charge of 6C that causes a force of 800N. What is the magnitude of the electric field? Do Now (9/17/13): A proton is placed in a uniform electric field of 200 N/C. Determine its: 1. Force 2. Acceleration Potentially useful info: mp=1.67x10-27kg me=9.1x10-31kg Electric Field Lines of a positive and negative charge Electric Field Lines of two Positive Charges Electric Field Lines Lines that indicate the strength and direction of the electric field. The more dense the lines, the stronger the field. Electric field vectors are tangent to the curve. Simulation http://online.cctt.org/physicslab/content/applets/ pointcharges/elefi_z.htm Field Lines should be evenly spaced! Which field is stronger? A B Consider the electric field lines shown in the diagram below. From the diagram, it is apparent that object A is ____ and object B is ____. a. +, + b. -, - c. +, - d. -, + e. insufficient info Practice: Use the rest of class to complete the paper “Electric Field Lines.” When you finish, submit to Ms. Timson If you finish early, please work on the bonus or your quiz review. Do Now (9/18/13): Use your understanding of electric field lines to identify the charges on the objects in the following configurations Practice: Use the rest of class to work on your quiz review and notecard! Conductors and Electric Fields (under electrostatic conditions) “The electric field is zero inside a charged conductor”. “Excess charge on an isolated conductor resides on the surface”. “Excess charge accumulates on sharp points”. Electric field lines meet the conductor perpendicular to the surface of the conductor. Shielding The electric field is zero inside a charged conductor. Where are you safe during a thunderstorm? A) In a car B) Outdoors or Why can you not get radio reception in a tunnel or in a steel bridge? Electric Field for a Point Charge Using E=F/qo and Coulomb’s Law prove: E=k Q ______ r2 where Q is the central charge. Example 2 A test charge of +3µC is located 5m to the east of a -4µC charge. A) Find the electric force felt by the test charge. B) Find the electric field at that location. Answer: 4.32x10-3 N, 1.44 x 103 N/C along the –x axis. Example 3 If a test charge is moved to a location three times as far as its original location, how does the electric field change? Example 4 Calculate the electric field felt by a test charge located half way between a charge of +1C and a charge of -3C, that are 2m apart. Answer: 1.8 x 1010 N/C