* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Immune System
Transmission (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Social immunity wikipedia , lookup
Sociality and disease transmission wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Childhood immunizations in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Globalization and disease wikipedia , lookup
Sjögren syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Herd immunity wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Food allergy wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
HIV vaccine wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
Immunocontraception wikipedia , lookup
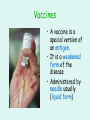
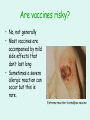
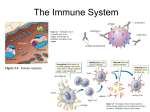
Ch 3 – The Immune System 3.2 Factors Affecting the Immune System Immunity • Recall: if our bodies contain the antibodies for specific antigens, we have what is called “immunity”. • We develop immunity when we get sick and our body makes antibodies to fight an antigen. • We can also obtain immunity by receiving a vaccine (vaccination). Vaccines • A vaccine is a special version of an antigen. • It is a weakened form of the disease • Administered by needle usually (liquid form) How do vaccines work? • A small amount of weakened disease enters the body • Your immune system creates antibodies to fight the disease • You don’t become ill because there is such a small amount of weakened disease • But some antibodies remain… – They can be reactivated if the antigen enters your body in the future More about vaccines • Vaccines can be a one-shot deal or you may get another vaccination every few years. • For example, we get tetanus shots every 10 years to bolster antibody production. • Some vaccines you receive as a baby Are vaccines risky? • No, not generally • Most vaccines are accompanied by mild side effects that don’t last long • Sometimes a severe allergic reaction can occur but this is rare. Extreme reaction to smallpox vaccine Disorders of the Immune System • Some people have an unusually high sensitivity to a certain substance. – When the substance enters their body, the immune system recognizes it as an invader and the system over-reacts! – This sensitivity is called an allergy Allergies • There are many things that can cause allergies. – Food (milk, gluten, peanuts, strawberries…) – Pollen, dust – Cats, beestings Any substance that causes an allergic reaction is called an “allergen”. Did You Know? • Dust allergies may actually be due to the feces of dust mites that live in house dust! • Dust mites eat dead skin flakes and make their home in your bed, carpet and old clothing! Allergy Symptoms • Common symptoms of an allergy – Runny nose – Watery eyes • Why does this happen? • When your body needs to fight an invader (an allergen) it releases a chemical called histamine • Runny noses and watering eyes are side-effects of histamine • We use drugs called anti-histamines to reduce these symptoms Severe Allergic Reactions • Some people have more severe allergies – Ex: peanuts, bee-stings • If they come in contact with these allergens they can have a severe reaction called anaphylactic shock • Results in swelling, difficulty breathing, can be fatal • People often carry adrenaline-shots (EpiPen) to reduce the effects. Disorders of the Immune System • AIDS – Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome • Infection of the immune system that can lead to death • Caused by a virus called human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) • HIV is a fierce pathogen that attacks the immune system and destroys it What does HIV do to the body? • HIV infects helper T cells – Since helper T cells activate B cells, your body can no longer activate B cells or killer T cells – The immune system has no way to fight the pathogen – In other words, the immune system shuts down – Other antigens or pathogens can enter and your body has no way to fight against them How is HIV transmitted? • HIV can be transmitted through – Blood – Semen • HIV cannot be transmitted through – Direct contact • Shaking hands – Saliva • Sharing drinks, kissing Cure for AIDS? • There is currently no known cure for AIDS • HIV keeps changing its structure slightly • There are also several forms of the virus • A person infected with HIV live 4-10 years • AIDS currently affects more than 40 million people Keeping Your Immune System Healthy • What can you do? – – – – – – – – Eat healthy foods Exercise Wash your hands Keep yourself and your home clean Avoid drugs/ tobacco Get enough sleep Get vaccinations Be cautious (don’t share drinks, etc..)