* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 8
Survey
Document related concepts
Major histocompatibility complex wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Sjögren syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Duffy antigen system wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
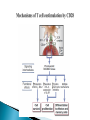
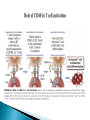
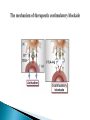
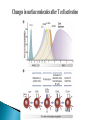
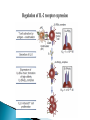
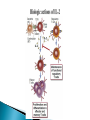
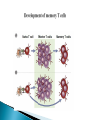
Activation of T Lymphocytes Activation and effector phases of T cell-mediated adaptive immune responses are triggered by antigen recognition by T lymphocytes Naive T lymphocytes home to secondary lymphoid organs, where they may encounter antigens presented by mature dendritic cells on class I or class II MHC molecules and thus become activated Antigen-stimulated T cells that have received both "signal one" through the antigen receptor and "second signals" via co-stimulatory receptors may be induced to secrete cytokines and to express cytokine receptors (like IL-2) T cell responses decline after the antigen is eliminated by effector cells The proliferation of T lymphocytes and their differentiation into effector and memory cells require antigen recognition, costimulation, and cytokines Antigen is always the necessary first signal for the activation of lymphocytes, ensuring that the resultant immune response is specific for the antigen Activation of naive T cells requires recognition of antigen presented by dendritic cells Elimination of antigen leads to contraction of the T cell response, and this decline is responsible for maintaining homeostasis in the immune system Costimulation and growth factors like IL-2 stimulate expression of the antiapoptotic proteins Bcl-2 and Bcl-XL in the activated lymphocytes, and these proteins keep cells viable The inhibitory receptors CTLA-4 and PD-1, apoptosis induced by death receptors of the TNF receptor superfamily (such as TNFRI and Fas), and regulatory T cells