* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PowerPoint 演示文稿
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Inflammation wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Behçet's disease wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Complement system wikipedia , lookup
Infection control wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Neuromyelitis optica wikipedia , lookup
Pathophysiology of multiple sclerosis wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Management of multiple sclerosis wikipedia , lookup
Multiple sclerosis research wikipedia , lookup
Sjögren syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Acute pancreatitis wikipedia , lookup
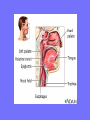
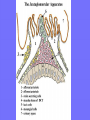
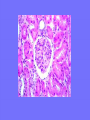
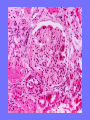
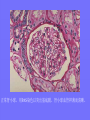
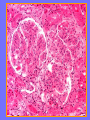
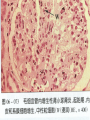
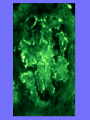
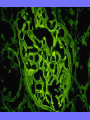
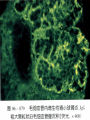
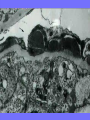
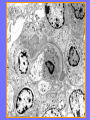
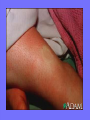
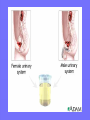
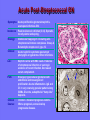
Acute Glomerular Nephritis Mao Jianhua, Department of Nephrology, The Children’s Hospital of Zhejiang University School of Medicine DEFINITION EPIDEMIOLOGY APSGN is a disease that affects primarily children, with the peak incidence being between ages of 2 and 6 years, Males are more likely than females to have overt nephritis. ETIOLOGY Nephritogenic strains of β– hemolytic streptococci PATHOGENESIS 1. Immune complex glomerulonephritis caused by deposition of circulating antigen-antibody complexes. 2. Autoimmune glomerulonephritis caused by deposited IgA being directed against a mesangial antigen or neo-antigen. 3. Immune complexes are formed in situ in the mesangium in response to a planted antigen. PATHOLOGY Endocapillary proliferative nephritis Light microscopy the glomeruli are found to be swollen and filled with cells obscuring much of the delicate network of the normal glomerular tugt. 正常肾小球,用PAS染色以突出基底膜。肾小球血管袢薄而清晰。 Immunofluorescence microscopy Glomerular deposits of IgG and C3 in capillary and mesangium Electron microscopy 1.The proliferation of cells is seen to involve primarily endothelial cells and the mesangium. 2.Electron-dense humps on the epithelial side of the basement membrane. Clinical Features Classically: 1. Edema and oliguria 2. hematuria 3. hypertension In some patients 1. Hypervolemia 2. Encephalopathy 3. Oilguric acute renal failure LABORATORY FEATURE ■ Complement:C3, CH50 ■ Blood ■ Renal function examination ■ ESR ■ urinalysis ■ ASO, ADNase-B, Ahase, et al. Differential diagnosis Rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis Chronic glomerulonephritis Infection-associated glomerulonephritis not caused by streptococcus Secondary glomerulopathies TREATMENT Treatment of acute PSGN is largely that of supportive care 1. Stay in Bed 2. DIET CONTROL 3. ANTIBIOTICS 4. Symptom control diuretics and anti-hypertension therapy 1. Congested circulation 2. Encephlopathy 3. Acute renal failure PROGNOSIS Most children (up to 95%) fully recover from APSGN in a matter of weeks or months. In those who do not recover fully, chronic or progressive problems of kidney function may occur. Kidney failure may result in some patients. Acute Post-Streptococcal GN Synonyms: Acute proliferative glomerulonephritis, acute post-infectious GN. Incidence: Peak incidence in children (3-14). Sporatic, mostly winter and spring. Etiology: Glomerular trapping of circulating antistreptococcal immune complexes. Group A, B-hemolytic streptococci, type 12. Acute nephritic syndrome post-strept pharyngitis or pyoderma. Other infections. Clinical: Lab: Path: Clinical Course: Nephritic urine with RBC casts. Evidence of streptococcal infection or serologic evidence of recent infection. Decreased serum complement. Enlarged, hypercellular glomeruli with endothelial and mesangial cell proliferation. Acute inflammation. IgG and C3 in very coarsely granular pattern along GBMs. Discrete, subepithelial “hump-like” deposits. Children - Excellent prognosis. Adults Worse prognosis, some develop progressive disease. Post-Streptococcal GN CNS Streptococcal Infection + Strep Assay Hypertension Latent Period Edema Proteinuria Acute Nephritis Hematuria