* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Vicksburg - Haiku Learning
Battle of Perryville wikipedia , lookup
First Battle of Lexington wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Appomattox Station wikipedia , lookup
Battle of White Oak Road wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Economy of the Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
Arkansas in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Big Bethel wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Forts Jackson and St. Philip wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Cumberland Church wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Namozine Church wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Donelson wikipedia , lookup
Fort Fisher wikipedia , lookup
Ulysses S. Grant and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Wilson's Creek wikipedia , lookup
First Battle of Bull Run wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Shiloh wikipedia , lookup
Battle of New Bern wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Seven Pines wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Lewis's Farm wikipedia , lookup
Second Battle of Corinth wikipedia , lookup
Capture of New Orleans wikipedia , lookup
Red River Campaign wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Gaines's Mill wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Jubal Early wikipedia , lookup
Western Theater of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Island Number Ten wikipedia , lookup
Conclusion of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Pillow wikipedia , lookup
USS Mound City (1861) wikipedia , lookup
Anaconda Plan wikipedia , lookup
Vicksburg Campaign wikipedia , lookup
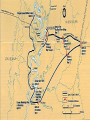
The Siege of Vicksburg took place form May 18 to July 4, 1863. Major General Ulysses S. Grant led a siege on the town of Vicksburg against the Confederate Lieutenant General John Pemberton. Grant commanded 77,000 troops against Pemberton’s 20,000. The Siege of Vicksburg took place because Grant wanted a strategic fort by a bend of the Mississippi River. Vicksburg also had railroads leading to Richmond and Jackson. The Union forces, under Grants control, came down the Mississippi River towards Vicksburg and then they left at Milliken’s Bend for Roundaway Bayou. They went south past Brierfield to cross the Mississippi at Bruinsburg. They then traveled east to fight the Confederates west of port Gibson on May 1, 1863. After securing fort Gibdson, they headed northeast for eleven days until fighting the Confederates at Raymond. They continued to Jackson, fighting again two days later. After that they traveled west, fighting the Confederates at Champion Hill and the Big Black River Bridge until reaching Vicksburg on May 18 where Pemberton already lay. The significance of the Siege of Vicksburg was that it cut off Confederate supplies lines and split the Confederacy in half. The claiming of Vicksburg would help Lincoln’s assessment and Scott’s Anaconda Plan. On July 4, 1863 the Union found themselves victorious in claiming Vicksburg. This was the last major city along the Mississippi River the Union needed to claim the entire river. Many thought of it as the turning point of the Civil War. The Siege of Vicksburg wasn’t an open-raged battle, it was fought mostly with artillery and was basically a bombardment on Confederate troops trapped within the city. The entire time the Union soldiers were fighting outside the city, leaving the Confederates inside to lose to disease and starvation. Pemberton eventually requested surrender on July 3. The long-lasting effects of the Siege of Vicksburg was that it successfully split the Confederacy in half, a major achievement for the Union. After securing Vicksburg they were able to then go for the Confederate capital, eventually leading to the Union’s victory of the Civil War. At the end of the battle, the Confederates had lost a total of 1,413 men and another 3,800 of them had gone missing. 3,878 were wounded in total. The Union suffered a loss of 1,581 dead men, and 1,007 deserters. 7,554 men were wounded.