* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Erwin Schrodinger an Max Born and wavelength
Angular momentum operator wikipedia , lookup
Quantum fiction wikipedia , lookup
Spin (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Coherent states wikipedia , lookup
Canonical quantum gravity wikipedia , lookup
Quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Quantum gravity wikipedia , lookup
Measurement in quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Mathematical formulation of the Standard Model wikipedia , lookup
Theory of everything wikipedia , lookup
Standard Model wikipedia , lookup
Eigenstate thermalization hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization group wikipedia , lookup
Wave packet wikipedia , lookup
Quantum entanglement wikipedia , lookup
Quantum chaos wikipedia , lookup
Matrix mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Quantum potential wikipedia , lookup
Quantum vacuum thruster wikipedia , lookup
Identical particles wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Path integral formulation wikipedia , lookup
Quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Photon polarization wikipedia , lookup
History of quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
Ensemble interpretation wikipedia , lookup
Bell's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Quantum tunnelling wikipedia , lookup
Probability amplitude wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Relational approach to quantum physics wikipedia , lookup
Electron scattering wikipedia , lookup
Symmetry in quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Quantum state wikipedia , lookup
Quantum logic wikipedia , lookup
Canonical quantization wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Old quantum theory wikipedia , lookup
Double-slit experiment wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
EPR paradox wikipedia , lookup
Uncertainty principle wikipedia , lookup
Interpretations of quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
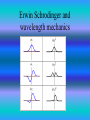
Erwin Schrodinger and Max Born and wavelength mechanics and quantum mechanics By: Will Gaul and Stevie Taylor Biography • August 12, 1887 – January 4, 1961 • Austria and Germany • Worked at University of Zurich, Friedrich Wilhelm University, and University of Oxford • Max Wien, Max Planck, Albert Einstein Erwin Schrodinger and wavelength mechanics • In 1926 he determined that a particle or an atom would vibrate in circles with activity • The atom contained, “Waves of Chance” • When an electron passed through the nucleus these waves would ripple back and forth • They would ripple in a straight line when particles moved through space inside an atom Erwin Schrodinger and wavelength mechanics Erwin Schrodinger and wavelength mechanics • proposed an original interpretation of the physical meaning of the wave function and in subsequent years repeatedly criticized the conventional Copenhagen interpretation of quantum mechanics Erwin Schrodinger and wavelength mechanics Quantum Theory • theoretical framework for constructing quantum mechanical models of subatomic particles in a particle physics and quasiparticles in condensed matter physics, by treating a particle as an excited state of an underlying physical field. Copenhagen Interpretation • an interpretation of quantum mechanics developed by Niels Bohr and his colleagues at the University of Copenhagen, based on the concept of wave-particle duality and the idea that the observation influences the results of an experiment Probability Density Function • Describes a cloud-like region where the electron is likely to be found. • It can not say with any certainty, where the electron actually is at any point in time, yet can describe where it ought to be • Known as probability cloud Electric Motion • Involves the Quantum Mechanical motion of rigid particles about some other mass, or about themselves. Orbital motion is characterized by orbital angular momentum and spin Sources • "Erwin Schrödinger - Biographical". Nobelprize.org. Nobel Media AB 2013. Web. 6 Nov 2013. <http://www.nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/physics/laureates /1933/schrodinger-bio.html> • Wagon, Joy. "The Cloud Model." The Cloud Model. N.p., 1999. Web. 06 Nov. 2013. • "Famous Scientists." Science Blog RSS. Famous Scientists, n.d. Web. 06 Nov. 2013. • Dingrando, Laurel. Chemistry: Matter and Change. New York, NY: Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, 2005. Print.