* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 5 Lesson 1
Efficient energy use wikipedia , lookup
Dark energy wikipedia , lookup
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
William Flynn Martin wikipedia , lookup
Open energy system models wikipedia , lookup
Energy subsidies wikipedia , lookup
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
100% renewable energy wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
Public schemes for energy efficient refurbishment wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
Gibbs free energy wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
Energy harvesting wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
United States energy law wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in British housing wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
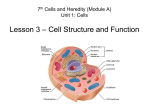
Unit 5 Lesson 1 What Is Energy? Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 5 Lesson 1 What Is Energy? Florida Benchmarks • SC.5.P.10.1 Investigate and describe some basic forms of energy, including light, heat, sound, electrical, chemical, and mechanical. • SC.5.P.10.2 Investigate and explain that energy has the ability to cause motion or create change. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 5 Lesson 1 What Is Energy? Energy All Around • Energy is the ability to cause changes in matter. • Energy can transform, or change, from one form into another. • Energy is never used up. It just changes form. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 5 Lesson 1 What Is Energy? The Ups and Downs of Energy • Potential energy (PE) is the energy an object has because of its position or condition. • Kinetic energy (KE) is the energy an object has because of its motion. • PE is stored energy. KE is energy of motion. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 5 Lesson 1 What Is Energy? The Ups and Downs of Energy • Energy can be stored as chemical energy. • Potential energy can be changed to kinetic energy. • Kinetic energy can be changed to potential energy. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 5 Lesson 1 What Is Energy? Loud, Soft, Hot, Cold • Sound energy is a form of energy that is carried as waves in vibrating matter. • Sound energy is a type of kinetic energy, because particles of matter are moving. • Sound energy is the cause of all the sounds you hear. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 5 Lesson 1 What Is Energy? Loud, Soft, Hot, Cold • Thermal energy is the total kinetic energy of the particles that make up a substance. • You can sense thermal energy as temperature. • The more thermal energy an object has, the greater its temperature. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 5 Lesson 1 What Is Energy? See a Sea of Energy • Light energy is a form of energy that can travel through space. • Light energy travels as waves. • Some objects give off light. Other objects reflect light. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 5 Lesson 1 What Is Energy? See a Sea of Energy • Electrical energy is energy caused by the movement of electric charges. • Electrical energy can change to other types of energy you can use. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 5 Lesson 1 What Is Energy? Energy in Machines and Food • Mechanical energy is the total energy of motion and position of an object. • Mechanical energy = KE + PE • Machines use mechanical energy to do work. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 5 Lesson 1 What Is Energy? Energy in Machines and Food • Food contains energy. • Chemical energy is energy that is stored in matter and that can be released by a chemical reaction. • When your body breaks down food, potential chemical energy is released, producing heat. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 5 Lesson 1 What Is Energy? Spotlight on Energy • Musicians and performers rely on different forms of energy to complete their shows. • Potential, kinetic, chemical, light, heat, mechanical, and sound energies are used. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company