* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Hinduism
Dharmaśāstra wikipedia , lookup
Indra's Net (book) wikipedia , lookup
Rajan Zed prayer protest wikipedia , lookup
Buddhism and Hinduism wikipedia , lookup
California textbook controversy over Hindu history wikipedia , lookup
Ardhanarishvara wikipedia , lookup
Hinduism in Indonesia wikipedia , lookup
History of Shaktism wikipedia , lookup
Invading the Sacred wikipedia , lookup
Neo-Vedanta wikipedia , lookup
Women in Hinduism wikipedia , lookup
Brahma Sutras wikipedia , lookup
History of Hinduism wikipedia , lookup
Tamil mythology wikipedia , lookup
Vishishtadvaita wikipedia , lookup
Pratyabhijna wikipedia , lookup
Hindu–Islamic relations wikipedia , lookup
Hindu views on evolution wikipedia , lookup
Hindu deities wikipedia , lookup
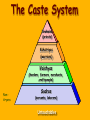
– Belief systems developed with the earliest humans, who saw the world as being full of spirits. – With the development of civilization, more complex belief systems developed – Hinduism developed in India – What type of jobs did untouchables perform under the caste system in India The Caste System Brahmins (priests) Kshatriyas (warriors) Vaishyas (herders, farmers, merchants, craftspeople) NonAryans Sudras (servants, laborers) Untouchables Hinduism Hinduism • One of the world’s oldest religions – Over 3,000 years old • No single founder – Formed from the beliefs of the diverse groups who settled in India • Original people of the Indus valley • Aryans Origins • Developed from the Vedas – 3500 – 2500 years ago – Polytheism • rituals and many gods – Sacred texts – The Caste System Brahman • One universal spirit • Appears as many different gods – This gave people a concrete way to worship and understand an impersonal god Atman • The individual soul of human beings Moksha • Ultimate goal of Hinduism • Union with the universal spiritual force (Brahman) – Release from worldly cares and difficulties • Atman + Brahman = Moksha Reincarnation • Sometimes called Samsara • Atman is reborn into the world after death • Continues until union with the Brahman Dharma • Spiritual and moral duties that must be followed Karma • All of the deeds of a person’s life • Allows people to continue towards Brahman • Goods deeds – Reincarnated into a higher castes • Bad deeds – Reincarnated into a lower caste or stuck in the same level Sacred Texts • Vedas • Upanishads – Nature of the world and meaning of life • Ramayana and Mahabharata – Epic poems – Discuss importance of following dharma Hindu Gods • Brahma – The god of creation Hindu Gods • Vishnu – The preserver god • Appears as ten different avatars Krishna with his consort Radha ; appears in the Mahabharata Shiva • God of destruction • Constructive destruction Shiva with his wife, Parvati, and his son Ganesha How Ganesha got his Elephant Head • Parvati (Ganesha’s mom) told him to stay outside her bath and allow no one to enter • Shiva arrived, and because he had been away for a long time, Ganesha didn’t recognize his dad • When Ganesha refused to allow Shiva to enter, Shiva cut off his head • Parvati refused to allow Shiva into her bedroom unless Ganesha was returned to life • Shiva took the head from the next animal to appear, and restored Ganesha to life with an elephant’s head All of the many Hindu deities are manifestations of the spirit Brahman Closure • What is the ultimate goal of Hinduism? • What is the connection between reincarnation and the caste system? • Identify one sacred Hindu text.