* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Spinal Cord and Reflexes Notes
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience in space wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
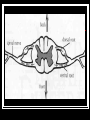
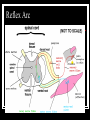
Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Somatic Reflexes Functions of the Spinal Cord Conduction – sends information up and down the cord Locomotion Reflexes – involuntary responses to stimuli The Spinal Cord is continuous with the brain and emerges from the foramen magnum at the base of the skull stretches downward for approx. 42 - 45 cm through the vertebral foramen there are 31 pairs of spinal nerves that emerge from the spinal cord through the intervertebral foramen Reflexes: the simplest responses to a stimulus Ex. Sneezing and Blinking produces a rapid motor response to a stimulus because the Sensory Neuron synapses directly with a motor neuron in the Spinal Cord. are very fast and most never reach the brain Meninges Enclose the spinal cord Three layers Dura mater – superficial Arachnoid mater Pia mater – deep Space between Epidural – between dura mater and vertebral bone Subarachnoid – between arachnoid and pia mater 2 Types of Nerves Radiating from Spinal Cord the dorsal roots contain Neurons that carry signals to the CNS from various kinds of Sensory Neurons (Affectors). the ventral roots contain the Axons of Motor Neurons, which are neurons that contact and carry information to the Muscles and Glands (Effectors). Gray Matter and White Matter 2 TYPES OF MATTER WITHIN SPINAL CORD Gray Matter Site of information processing Contains primarily unmyelinated structures Dendrites Synapses Looks like a butterfly 2 dorsal horns 2 ventral horns Central canal White Matter Carry signals fromone aprt of CNS to another Contains myelinated structures Primarily axons Surrounds the gray matter Bundles of axons that provide avenues of communication up and down the spinal cord Reflexes What is a reflex? Four properties of a reflex Stimulation – response to sensory input Quick Involuntary Sterotyped (predictable response) Reflex Arc