* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Brain and Behavior
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Apical dendrite wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
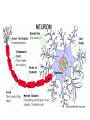
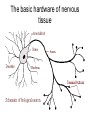
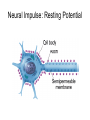
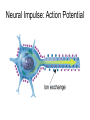
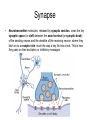
The Brain and Behavior Basic terminology • • • • Neuron – receive, integrate, transmit info signals Soma – (Greek for body) cell body Dendrites – specialized to receive info Axon – thin fiber that transmits signals away from soma to other neurons, muscles or glands • Myelin sheath – insulating material encasing axons • Glial cells (Schwann’s cells) – make myelin sheath • Terminal buttons – secrete neurotransmitters The basic hardware of nervous tissue DIFFERENT TYPES OF NEURONS • Sensory neurons or Bipolar neurons carry messages from the body's sense receptors (eyes, ears, etc.) to the CNS. • Motoneurons or Multipolar neurons carry signals from the CNS muscles and glands. • Interneurons or Pseudopolare (Spelling) cells form all the neural wiring within the CNS. These have two axons (instead of an axon and a dendrite). One axon communicates with the spinal cord; one with either the skin or muscle. GLIAL CELLS • • • • Glial cells make up 90 percent of the brain's cells. Glial cells are nerve cells that don't carry nerve impulses. The various glial (meaning "glue") cells perform many important functions… including: – digestion of parts of dead neurons, – manufacturing myelin for neurons, – providing physical and nutritional support for neurons Neural impulse • Electrochemical reaction • + charged sodium and potassium ions – charged chloride ions flow back and forth across the cell membrane • They do not cross at the same rate Neural Impulse: Resting Potential Neural Impulse: Action Potential Synapse • Neurotransmitter molecules, released by synaptic vesicles, cross the tiny synaptic space (or cleft) between the axon terminal (or synaptic knob) of the sending neuron and the dendrite of the receiving neuron, where they latch on to a receptor site, much the way a key fits into a lock. This is how they pass on their excitatory or inhibitory messages.