* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download World War II : The World at War
Collaboration with the Axis Powers wikipedia , lookup
Allied Control Council wikipedia , lookup
Appeasement wikipedia , lookup
Military history of Greece during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Allied plans for German industry after World War II wikipedia , lookup
Swedish iron-ore mining during World War II wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Battle of the Mediterranean wikipedia , lookup
Historiography of the Battle of France wikipedia , lookup
German military administration in occupied France during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
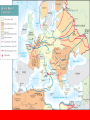
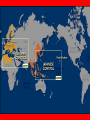
World War II : The World at War Neutral United States • 1920s-1930s U.S. practiced isolationism (kept out of international affairs) • President Franklin D. Roosevelt and Congress passed the Neutrality Act of 1939 declaring its wish to isolate itself from overseas conflicts Lend-Lease • Despite its neutrality, U.S. helped Britain hold off Hitler’s forces – Cash and Carry policy : U.S. offered to sell arms if Britain paid cash AND transported weapons in their own ships – Lend-Lease Act of 1941 : authorized prez to lend or lease goods to any country if they were helping to defend the U.S. Anti-Japanese trade ban • Japanese aggression against China, French Indochina, & the Dutch East Indies led to strong protests in U.S. • 1940 : President FDR banned all export of materials vital (necessary) to Japanese industry – ban included petroleum (gas) & scrap metal Blitzkrieg • 1940 - Hitler uses Blitzkrieg (lightning war) tactics = crushed opposing forces with speed and mobility – Troops & artillery in vehicles aided by planes and tanks • April 1940 – Germany conquers Norway & Denmark, then Belgium & Holland in May Invasion of France • June 1940 - French surrendered & Italy enters war • Germany splits France into 2 parts: – Occupied France & Vichy France • Occupied France = controlled by German forces • Vichy France = French fascist paramilitary organization, The Milice Britain stands alone • United States remains neutral, but sent food and arms to British • Britain aided by its colonies and former colonies Battle of Britain • August 1940 – Germans begin bombing British cities, industrial areas, seaports, & military installations • Prime Minister Winston Churchill inspired British people • British Royal Air Force destroyed large numbers of German planes • June 1941 – aid raids eased off Eastern Front • Late 1940 – Hungary and Rumania joined Axis Powers, Bulgaria in 1941 • Yugoslavia & Greece defeated; Germans control all of the Balkans Soviet Union • June 1941 – Hitler invades Soviet Union – Germans wanted farmlands and oil • Britain & U.S. aided the Soviets w/ food & arms – December – Soviet army counterattacks = winter weather halts Germans Pearl Harbor • U.S. ban = Japan’s oil supplies drop = Japan gets desperate • December 7, 1941 – Japanese planes bombed U.S. Naval Base at Pearl Harbor in Hawaii – Most of U.S. fleet destroyed or severely damaged • President Roosevelt requests declaration of war on Japan = Congress agrees December 8, 1941 – 3 days later : Germany & Italy declared war on U.S. Allied Strategy in Europe • Jan. 1942 : U.S., Britain, Soviet Union, & 23 nations sign Declaration of United Nations – Strategy : concentrate on Europe first, then Pacific • North Africa – 1942-1943 : Allied Powers fight Germans to win back whole of North Africa by May • Eastern Front – 1943 : Germans suffer defeat at Stalingrad – Russians pushed Germany west all the way to Berlin, Germany in April 1945 Italian Campaign • July 1943 - Allies invade Sicily – Mussolini forced out of office & imprisoned by Italian King (later shot & dragged through streets) • Italians join Allies, but Germans continue to fight – 1944 : Rome fell to Allies – 1945 : German loses Northern Italy D-Day • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3wUjZpPNsxI • June 6, 1944 – U.S. General Eisenhower led Allied troops across English Channel to shores of Normandy, France • Americans pushed Germans out of France, Belgium, and Holland – Dec 1944 : Germany’s last offense in Battle of the Bulge in Belgium, but quickly pushed back into Germany Fall of Hitler • March 1945 : Allies move into Germany from west as Soviets move into Berlin from east – Hitler committed suicide • May 7 : German leaders surrender – Next day : V-E Day (Victory in Europe) declared