* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download No Slide Title
Historiography of the Battle of France wikipedia , lookup
German–Soviet Axis talks wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Fascism in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Operation Torch wikipedia , lookup
Allied Control Council wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied plans for German industry after World War II wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
Military history of Greece during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Italian resistance movement wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Operation Bodyguard wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Battle of the Mediterranean wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Invasion of Normandy wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
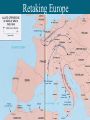
Retaking Europe August 1941 FDR and Winston Churchill met in secret on a warship off of Newfoundland to guide them in the years ahead. Became the basis for the United Nations. When the U.S. entered the war in 1941, it was a critical time for the Allies: • Britain suffered major bomb damage. • German blitzkrieg extended Nazi control across most of Europe. • In North Africa, German and Italian forces were bearing down on British forces. Many people feared that Germany could not be stopped. Battle of the Atlantic Wolf packs were groups of as many as 20 U-boats which attacked Allied convoys of military and merchant ships and caused trouble in the Atlantic. North Africa Campaign 1941-1943 General Eisenhower General Rommel “Desert Fox” The Italians with German help had pushed deep into British controlled Egypt and threatened the Middle East. The U.S. arrived in Nov, 1942. Operation Torch Nov. 1942 By May 1943, the Allies had the Axis forces in N. Africa trapped. Despite Hitler’s demands not to, about 240,000 Germans and Italians surrendered. German Advance As the Allies battled their way across North Africa in the and into Italy, an epic battle Soviet Union raged in eastern Europe. 1941-42 Looking for “living space,” Hilter broke his pact with Stalin and began a plan to seize farmland in the Ukraine. Operation Barbarossa Stalin asked for and received U.S. aid through the Lend-Lease Act. Stalin ordered a “scorched earth” policy for any retreating Soviet troops. Stalin desperately urged the other Allies to launch an attack on Western Europe (France). This would take pressure off the Soviet Union by forcing Hitler to fight a two-front war. Churchill persuaded FDR to attack through Italy, Europe’s “soft under-belly” instead. Battle of Stalingrad Nov. 1942 January 1943 90,000 Germans surrendered; Turning point of the war in 330,000 Germans Eastern Europe. USSR began perished; Soviet losses a long struggle to regain could be as high as territory lost to Germany. 1,100,000 Casablanca Conference, January 1943 Churchill and FDR meet again in Casablanca, Morocco. They map out their strategy for the rest of the war…continuing the course of concentrating Allied resources in Europe Nothing but Germany’s “unconditional surrender” before trying to win will do to end the war. the war in the Pacific. Invasion of Italy July 1943 In July 1943, U.S. 7th Division, under General George S. Patton, invaded Sicily with British forces. The Italians lost faith in Mussolini. He was arrested and removed from office. The German’s free him and evacuated him to Northern Italy. Invasion of Italy July 1943 In September 1942, as the Allies threatened to overrun Rome, Italy’s new government surrendered. In October, the Italians declared war on Germany. The Germans set up Mussolini as a puppet ruler of a fascist Italian state in northern Italy. Mussolini was shot and killed by Italians as he tried to flee across the northern Italian border as the Allies advanced. The Allied Air War Carpet Bombing by the Allies caused severe damage in German cities. Allied Invasion of Western Europe In late 1943, the British finally agreed to go along with Stalin and FDR and invade Western Europe. Operation Overlord would be launched from Great Britain. General Eisenhower was named Supreme Commander of the Allied invasion forces. Landing at the Normandy Beaches D-Day June 6, 1944 Liberating France Charles de Gaulle immediately took charge of the French government. United States’ General Patton used blitzkrieg techniques to burst out of Normandy. He and his troops swept across Northern France. The French Resistance helped the U.S. 1st Division free Paris. Liberating France The Allies began to push the Axis powers back through Belgium and Luxembourg towards Germany. Battle of the Bulge December 1944 The Nazis fought desperately to defend their conquests in Europe. After being pushed out of France, the Germans mounted a counter-attack in Belgium & Luxembourg, the largest battle Europe. Battle of the Bulge The Nazis hoped to split the Allies in two. The Allies focused on cutting the Nazi supply lines. Fighting in terrible winter conditions, the Allies were finally able to defeat the Nazis. After the battle, most German leaders recognized that the war was lost. Yalta Conference February 1945 - Agreed to split Germany into four zones, each under control of a major Allied country. - Stalin promised FDR, Churchill and Stalin fair elections in E. European countries meet to plan the final defeat and participation in of Hilter and decide the shape of the post-war world. the Pacific theater. Soviet Forces Advance The Soviet Union had lost over 11 million soldiers during WWII (compared to Germany’s 3 million). After the hardships their country endured, Soviet leaders considered the capture of Berlin a matter of honor. Berlin falls in April 1945. Hitler commits suicide - Germany surrenders! May 1, 1945 Hitler and Eva Braun. Outside the underground bunker where Hitler died. V-E Day