* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download WORLD WAR II
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
German occupation of Czechoslovakia wikipedia , lookup
Naval history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Fascism in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Anglo-German Naval Agreement wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
German–Soviet Axis talks wikipedia , lookup
Historiography of the Battle of France wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
American Theater (World War II) wikipedia , lookup
Nazi views on Catholicism wikipedia , lookup
World War II and American animation wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Appeasement wikipedia , lookup
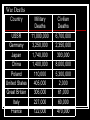
Put in notes! – Warm up! Chapter 26: Vocab Demilitarized Appeasement Sanction Blitzkrieg Partisan Genocide Collaborator Kamikaze Cold War WORLD WAR II THE CAUSES 4 slides “Aryan” Desires Expansion Hitler wanted to expand his Aryan ideal into neighboring countries in Europe U.S.S.R. Use the Russians as Slave Labor Austria Annexed March 13, 1938 Violating the Treaty of Versailles Hitler believed that the T of V was holding Germany back Ordered creation of an air force – Luftwaffe Order nation conscription Army increased from 100,000 to 550,000 Moves troops in to demilitarized zone of the Rhineland Western Allies warn, but do not use force Munich Conference Hitler desired the Sudetenland, a predominately German settled region of Czechoslovakia Meets with British, French, and Italians to reach agreement Hitler is given Sudetenland under promise that he will stop his advances. Poland Hitler wanted the Polish port of Danzig to attack Russia. U.S.S.R. approached for alliance Nazi-Soviet Non-Aggression Pact, 8/23/1939 France and U.K. could not fight Germany alone Hitler wants Stalin to think him as a friend Divided up Poland between Hitler and Stalin Promise to not fight each other Hitler invades Poland, 9/1/1939 France and U.K. declare war, 9/3/1939 WORLD WAR II The Course of War (5 slides) Blitzkrieg “Lighting War” Panzer divisions – 300 Tanks September 28, 1939 April 9, 1940 Poland conquered and divided Nazi-Soviet Non-Aggression Pact legal Denmark and Norway attacked May 10, 1940 Netherlands, Belgium Battle of Dunkirk France is attacked Germans go around Maginot Line where French were entrenched British and French troops are pushed back to the sea Massive evacuation across the channel to Britain, leaving all their supplies behind The Fall of France Armistice – June 22 Germans occupy most of Northern France The Battle of Britain Hitler plans to invade England August 1940 - Luftwaffe begins bombing British bases, harbors, communication centers, and factories Britain retaliates with an attack on Berlin. September 1940 – Hitler orders an attack on British cities, particularly, London. Gives England time to rebuild air forces Hitler eventually postpones invasion of Britain Help! Britain asks the United States for help Public - Isolationism World War I President - Involvement Neutrality encouraged aggression Supplies to Britain THE CAUSES OF WORLD WAR II The Treaty of Versailles, 1918 Hitler’s armament build up and militaristic expansion The Munich Conference Nazi-Soviet Non-Aggression Pact Attack on the Soviet Union Attack on USSR scheduled for Spring, 1941 Hitler was convinced Britain only stayed in the war hoping for Soviet relief Germany invades USSR June 22, 1941 Russian winter again victorious – Germans halt Japanese Aggression in the Pacific Attacks on China Chiang Kai-Shek Fighting Both Japan and the Communists Japanese conquer Manchuria, Beijing, Shanghai, and Hong Kong by 1941 Wanted economic resources U.S. threatens economic sanctions Japan’s Entrance 1941-42 - Almost all of South East Asia under Japanese control United States- “stop or face economic sanction” Japan attacks: U.S. Naval Base at Pearl Harbor, Hawaii, Dec. 7, 1941 World War II 1941-1945 (7 slides) New Alliances U.S., Great Britain, and U.S.S.R. The Big Three Roosevelt Churchill Stalin Unconditional surrender of the Axis North Africa November, 1942 – Germans and Italians surrender to Americans and British under Dwight D. Eisenhower. Stalingrad Nov 1942-Feb 1943 Costliest battle of the war 3 million German and Russian casualties German surrender Hitler abandons invasion of U.S.S.R., retreats The Pacific Midway – June 4, 1942 U.S. Navy defeats Japanese Navy “Revenge for Pearl Harbor” Douglas MacArthur U.S. Commander in Pacific “Island Hopping” D Day June 6, 1944 Allied invasion of Normandy Dwight D. Eisenhower (US) George Montgomery (UK) Troop stormed beaches Destruction of German defenses Paris Liberated August, 1944 The End - Europe Battle of the Bulge – Dec 1944 to Jan 1945 Heavy Bombardment of Berlin begins Adolf Hitler moves underground March 1945 – Allies Crossed the Rhine Adolf Hitler commits suicide on April 30. Germany surrenders May 7, 1945 – V-E Day The End - Pacific Roosevelt dies in office Harry S. Truman becomes president Only president to serve four terms 1ST Plan an invasion Battle of Iwo Jima Orders nuclear bombardment of Hiroshima and Nagasaki Japan Japan surrenders, August 14, 1945 The Enola Gay Drops the Bomb Celebration War Deaths Country Military Deaths Civilian Deaths USSR 11,000,000 6,700,000 Germany 3,250,000 2,350,000 Japan 1,740,000 393,000 China 1,400,000 8,000,000 Poland 110,000 5,300,000 United States 405,000 2,000 Great Britain 306,000 61,000 Italy 227,000 60,000 France 122,000 470,000