* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Battle of Coral Sea
Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Allied plans for German industry after World War II wikipedia , lookup
Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Swedish iron-ore mining during World War II wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
German–Soviet Axis talks wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Naval history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
Appeasement wikipedia , lookup
American Theater (World War II) wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
United States Navy in World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
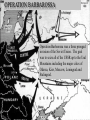
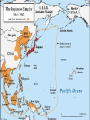
World War II The Other War to End All Wars… For now…. We hope…. Leading up to the War • • • • • • World War I Great Depression Rise of Fascism and Totalitarianism Appeasement Failure of the League of Nations Civil War in Spain (warm-up for war) The U.S. at the Beginning of WWII • Isolationist – Sick of war – Kellogg-Briand Pact outlawed war • Passed laws so that they would not sell weapons to ANY country at war. – Neutrality Act of 1936 to stay out of war. Key Players in the War Axis Powers • Adolf Hitler (GER) • Benito Mussolini (ITA) • Hideki Tojo (JAP) Allied Powers • Neville Chamberlain (GBR) • Winston Churchill (GBR) • Charles De Gaulle (FRA) • Franklin Roosevelt (USA) • Harry Truman (USA) • Joseph Stalin (USSR) Axis Powers (and Germany) The Painful Lesson • Great Britain, France, Italy, and Germany meet in Munich on September 28, 1938. • Hitler has been aggressive in taking land west of Germany • GB and FR try to appease Hitler by giving him the Sudetenland in Czechoslovakia, in hopes that Hitler would cease. • “agreement” is a failure. • Hitler invades the “demilitarized” Czechoslovakia and promptly breaks Munich Pact • By the end of 1939 both Hitler and Mussolini had conquered more territory in Europe and made plans for further wars. • Becomes famous as the “Lesson of Munich” 7 Appeasement • “My good friends, for the second time in our history, a British Prime Minister has returned from Germany bringing peace with honour. I believe it is peace for our time.” Neville Chamberlain Non-aggression pact • Germany and Soviet Union sign in 1939. • Agree not to attack one another. • This shocked the world: o WHY? Fascists and communists work together. • Secret provision was the dividing of Poland. • However, Hitler knew he would eventually invade Soviet Union. September 1st, 1939 Germany invades Poland officially beginning World War II • On September 1, 1939 Germany and the USSR launched a full-scale invasion of Poland. • Britain and France declared war on Germany and WWII had begun. • Germany and the Soviet Union divided Poland into two zones. • One month later Germany invaded France 10 France • Germany invaded through Belgium around the Maginot Line (heavily fortified section of the German-French border) in June of 1940. • • • • Took Paris 9 days later France was completely occupied within 6 weeks. Renamed “Vichy France.” HOWEVER- Denmark was taken in several HOURS Europe 1940 Britain Who’s Next? 12 Battle of Britain Summer of 1940 Germany began to bomb Britain’s cities to keep them out of the main fight. Britain had been a tough opponent in WWI and the Germans knew this. OPERATION BARBAROSSA Operation Barbarossa was a three pronged invasion of the Soviet Union. The goal was to seize all of the USSR up to the Ural Mountains including the major cities of Odessa, Kiev, Moscow, Leningrad and Stalingrad. 14 1941- Germany broke pact with USSR German invasion of USSR Soviets used a “scorched earth” policy to slow down the Germans, burning as they retreated (Remember Napoleon, anyone?). Battle of Stalingrad • July 1942 – February 1943 • Bloodiest battle in the history of warfare o 2 million casualties • German commander Paulus surrendered in Jan 1943. • Importance of German loss: o o Turning point of the war in Eastern Europe Germany would never go on offensive again against the USSR Turning Point in Europe • Battle of Normandy • Largest marine invasion ever. The Pacific Theater • Japanese expansion (1895-1938) • Attempted to take over Asia as the new imperial power • (1938-1945) During the war, Japanese had to protect oil shipments (no domestic oil resources). • U.S. was the lead power in the Pacific to fight Japan, U.S. supported China. • All other allies were finishing up in Europe. Embargo Against Japan Japan continued its aggression against China causing relations to erode with the US. Japan joined Germany and Italy in an anti-Soviet treaty. Despite US warnings to stay out of Indochina (Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia) Japan took control of the Asian territory. • Japan wanted the US to stop sending aid to China, and restore trade with Japan. Diplomatic talks in November 1941 failed, and during the meetings, Japan planned an attack on the United States. 19 •The surprise attack Pearl Harbor •onOn December Dec. 7, 1941 7, 1941 at 7:55 AM, destroyed 18Japanese bombers188 attacked the US warships, fleet atand Pearl Harbor, aircraft killed Hawaii. 2,403 servicemen at a Glance 20 Kamikaze • Means “Divine Wind” • Suicide attacks by warplanes from the Empire of Japan against Allied naval vessels in the closing stages of the Pacific campaign. • First used at Battle of Leyte Gulf (Philippines) • A total of 57 ships were sunk by the Kamikazes. The Battle of Coral Sea • The Battle of the Coral Sea was fought between the Japanese and Allied navies from May 4 through May 8, 1942 in the Coral Sea, about 500 miles northeast of Australia. • Occurring only six months after the surprise attack at Pearl Harbor, it was one of the first naval battles fought in the Pacific during World War II. Battle Of Midway • Decisive US victory –June 1942 at Midway Atoll • American codebreakers were able to determine the date + location of attack. • Four Japanese aircraft carriers were sunk in exchange for one American. • The heavy losses in carriers and aircrews permanently weakened the Imperial Japanese Navy. Maps of the devastation and the weapon that caused it First Atomic Bomb Format of the First Atomic Bomb Perspective on Bombings • A ground invasion of Japan would have cost between ½ million and 2 million American soldiers’ lives, according to military studies. • 150-200 thousand Japanese total casualties for both bombings. • 600,000+ had been killed by conventional bombing in the months prior to the A-bombs. Meetings at Yalta and Potsdam • • • • Stalin, Roosevelt, and Churchill met. Established a “plan” for the end of the war Included how new governments would be set up. Stalin assured others that democratically-elected governments would be set up. Occupation of Japan and Germany • Both countries rebuilt • Economies and industries rebuilt • U.S. made no territorial claims to either country Results