* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download WWII: Battlefront
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Anglo-German Naval Agreement wikipedia , lookup
Fascism in Europe wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied plans for German industry after World War II wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Nazi views on Catholicism wikipedia , lookup
Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Appeasement wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
European theatre of World War II wikipedia , lookup
World War II and American animation wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
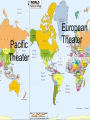
BEFORE the bell rings 1. 2. 3. 4. Turn in WS p. 249-250 and 255-256 to basket. Turn in Progress Report to basket. Turn in Extra Credit Answers to basket. Get a sheet of paper out and pen/pencil. EXTRA CREDIT-write answers in complete sentences. 1. 2. 3. What was the Schlieffen Plan? Who declared war on Austria-Hungry after A-H declared war on Serbia? What plan called for a just and lasting peace? In the future days, which we seek to make secure, we look forward to a world founded upon four essential human freedoms. The first is freedom of speech and expression—everywhere in the world. The second is freedom of every person to worship God in his own way—everywhere in the world. The third is freedom from want—which, translated into world terms, means economic understandings which will secure to every nation a healthy peacetime life for its inhabitants—everywhere in the world. The fourth is freedom from fear—which, translated into world terms, means a world-wide reduction of armaments to such a point and in such a thorough fashion that no nation will be in a position to commit an act of physical aggression against any neighbor—anywhere in the world. WWII: Battlefronts 1939-1945 Two Theaters: Europe (Germany) Pacific (Japan) Pacific Theater European Theater Axis Strategies Axis: Germany, Italy & Japan Main goal: prevent American war materials from getting into Europe… had their own goals only shared common enemies u-boats patrol seas (“wolf packs”) but sonar use will level the playing field Battle of Britain: German air raids on Britain… Hitler was hoping to defeat Britain just like he had France… not successful Allied Strategies Allies: France, Britain, China, US, Russia Had General George Patton controlling efforts in Africa Allies attacked Italy unified in their goals… get Hitler in Europe and then turn to the Pacific Mussolini overthrown removed Hitler’s help… new government declared war on Germany Russia wanted Allies to set up western front in France Germany was fighting a two-front war War in Europe: Stalingrad Germany attacked Russia (Why is this significant?) Hitler wanted Stalingrad for the oil fields Non-Aggression Pact Hitler would not admit defeat even though his troops were surrounded Turning Point of War In Europe ended any plans Hitler had for domination in Europe Operation Overlord (D-Day) Plan to invade German occupied France create two-front war for Germany led by General Dwight D. Eisenhower D-Day: when Allies hit Germany on the beaches of Normandy (code name Omaha) Now Germany fought a hopeless two front war with Allies closing in on Germany… this is why Germany lost the war Battle of the Bulge Germany’s counterattack to D-Day an attempt to separate British and American troops Not successful only pushed Hitler further back into Germany… defeat would come soon Ends war in Europe V-E (Victory in Europe) Day Hitler commits suicide on April 30, 1945 7 days later Germany surrendered on May 7th War in Pacific: Midway Japan was trying to conquer all of Asia… turned its sights to the American naval base at Midway American Admiral Chester Nimitz knew of these plans and dealt them the most decisive defeat of the war… turning point of war in the Pacific because it ended the Japanese advancement in the Pacific Island Hopping American strategy in the Pacific hop from island to island on a steady path to Japan Deadly process when Japanese kamikazes deliberately crash their planes into American ships Like suicide bombers Iwo Jima part of island hopping 36 day campaign to obtain the 5 mile island of Iwo Jima US Marines plant the American flag on Japanese territory… symbolic of American successes and later victory over Japan The Atomic Bomb Ends the War Albert Einstein split atoms and it created large amounts of energy… FDR creates the Manhattan Project to develop the atomic bomb for military use did not realize its potential and future impact on war would be so devastating bombs are tested in Arizona led by J. Robert Oppenheimer V-J Day President Harry Truman ordered for two atomic bombs to be dropped on the Japanese cities of Nagasaki and Hiroshima Emperor Hirohito surrendered and Americans celebrated VJ (Victory in Japan) Day WWII was over Holocaust Nazis attempt to kill all Jews (genocide) Hitler’s Final Solution to the Jewish problem extermination of all Jews 6 million total Concentration/death camps warehoused Jews until extermination After war, America helps liberate (free) remaining Jews WWII Meetings Casablanca Conference: first meeting between Allies (GB and US) to discuss war strategies Tehran Conference: 1st Big Three meeting on how to get Hitler to surrender Yalta Conference: end of war meeting on how to rebuild Europe and divide up Germany amongst Allies Potsdam Conference: meeting to discuss how to punish Germany and get Japan to surrender The Big Three Joseph Stalin for Soviet Union FDR for US, after he dies Harry Truman steps in. Winston Churchill for Britain