* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Evolution Lecture #1
Survey
Document related concepts
Objections to evolution wikipedia , lookup
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Acceptance of evolution by religious groups wikipedia , lookup
Hindu views on evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
The Expression of the Emotions in Man and Animals wikipedia , lookup
The Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex wikipedia , lookup
Transitional fossil wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
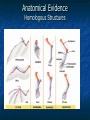
Evidence of Evolution 15.1 Blindfold Demo I. Evolution Definitions A. Evolution- Change in inherited traits of a POPULATION (not individuals) over time. B. Variation- Changes between members of the same species caused by DNA mutations. II. Charles Darwin A. It all began on the English ship, the HMS Beagle 1. Darwin worked as the naturalists 2. He took samples of living specimens and fossils II. Charles Darwin B. Darwin’s observations in the Galapagos Islands 1. Species are unique, yet similar to species elsewhere 2. Species produce many offspring, but don’t overrun the earth II. Charles Darwin 3. Individuals in a species struggle to survive a. Compete for food b. Compete for shelter c. Compete for water d. Etc II. Charles Darwin C. Pigeon experiments 1. Darwin realizes that he can select and breed specific pigeons to get a desired trait. II. Charles Darwin 2. Artificial Selection- Breeding organisms with specific traits in order to produce offspring with identical traits. a. Similar to a force in nature that causes changes II. Charles Darwin D. Natural Selection- Organisms with favorable traits for their environment survive and reproduce. Organisms without favorable traits die! 1. Survival of the fittest!!! 2. Causes changes in populations a. Car demo II. Charles Darwin E. Principles of Natural Selection 1. Organisms produce more offspring than can survive 2. Differences, AKA variations occur among individual species 3. Some variations are passed to the offspring II. Charles Darwin 4. Some variations are helpful and help organisms to survive and reproduce better. 5. Over time, individuals with the helpful variations make up more of the population and often becomes a separate species. RUEBEN VS. CARS DEMO III. Evidence for Evolution A. Adaptations that increase survival 1. Structural a. Body parts b. Camouflage c. Mimicry III. Evidence for Evolution 2. PhysiologicalChanges in metabolism a. Penicillin resistant bacteria b. Pesticide resistant insects III. EVIDENCE FOR EVOLUTION B. Fossils & Transition Fossils 1. Archeopteryx: intermediate between reptiles & birds 2. Eustheopteron: fish to amphibians 3. Seymouria: amphibian to reptiles 4. Therapsids: reptiles to mammals III. EVIDENCE FOR EVOLUTION C. Anatomical Evidence 1. Homologous StructuresStructure with similar origins (shape, function, etc) a. Provides evidence of common ancestor b. Ex: Forelimbs of whales, crocodiles and birds Anatomical Evidence Homologous Structures III. EVIDENCE FOR EVOLUTION 2. Analogous StructuresStructures that DO NOT have similar origin, but DO have similar functions a. Not closely related b. Wing of a butterfly and wing of a bird Anatomical Evidence analogous structures III. EVIDENCE FOR EVOLUTION 3. Vestigial StructuresStructures that no longer serve their original purpose 1. Ex: Human ear muscles, whale feet, blind mole-rat eyes Anatomical Evidence vestigial structures III. EVIDENCE FOR EVOLUTION 4. Embryology Evidence a. Embryo- Earliest stage of growth & development b. All embryos look similar Evidence from Embryology •http://www.exploratorium.edu/exhibits/embryo/embryo.html III. EVIDENCE FOR EVOLUTION 5. Biochemistry Evidence a. DNA is similar in all species b. Evidence of common ancestor III. EVIDENCE FOR EVOLUTION c. The more DNA alleles in common, the more closely related two organisms are! 1) Humans & chimps have 97% of the same DNA