* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Reflection - E. R. Greenman
Survey
Document related concepts
Nonlinear optics wikipedia , lookup
Reflector sight wikipedia , lookup
Optical flat wikipedia , lookup
Surface plasmon resonance microscopy wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric optics wikipedia , lookup
Photon scanning microscopy wikipedia , lookup
Optical telescope wikipedia , lookup
Magic Mirror (Snow White) wikipedia , lookup
Birefringence wikipedia , lookup
Image stabilization wikipedia , lookup
Ray tracing (graphics) wikipedia , lookup
Nonimaging optics wikipedia , lookup
Anti-reflective coating wikipedia , lookup
Harold Hopkins (physicist) wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
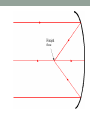
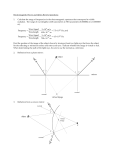
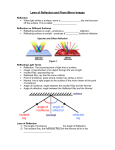
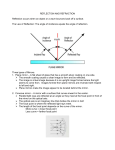
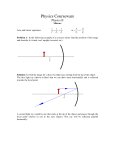
REFLECTION Physics Chapter 18a Law of Reflection Angle of incidence equals angle of reflection Reflection Change in direction of wave at interface between two media Reflecting surface smoothness controls type of reflection Specular: smooth surface, forms good image Diffuse: rough surface, does not form good image Reflections Example The angle of incidence of a light ray is 42o. What are: The angle of reflection The angle the incident ray makes with the mirror The angle between the incident ray and the reflected ray Plane Mirror Flat mirror Forms a virtual image at the same distance that the object is Virtual image is upright Mirror equation: 1/p + 1/q = 1/f p=object distance q=image distance f=focal length Plane Mirror Concave Mirror Concave mirror is curved away from observer Mirror reference points: Optical axis Normal at center of mirror Also called principal axis Focal point Point on optical axis where every reflected ray passes through Focal length: distance from mirror to focal point (along optical axis) Concave Mirrors • Reflections: • Rays parallel to principal axis reflect through focal point • Rays through focal point reflect parallel to principal axis • Rays through center (along principal axis) reflect back along same path How do we find where an image is? • Draw carefully!! How do we find where an image is? • Draw carefully!! How do we find where an image is? • Draw carefully!!