* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PP - snc2p_u4l6_climate_change_factors
ExxonMobil climate change controversy wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Climate resilience wikipedia , lookup
Snowball Earth wikipedia , lookup
Global warming controversy wikipedia , lookup
Climate change denial wikipedia , lookup
Climate change adaptation wikipedia , lookup
Heaven and Earth (book) wikipedia , lookup
Global warming hiatus wikipedia , lookup
Economics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Instrumental temperature record wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Tuvalu wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on human health wikipedia , lookup
Mitigation of global warming in Australia wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Fred Singer wikipedia , lookup
Climate governance wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Media coverage of global warming wikipedia , lookup
General circulation model wikipedia , lookup
Physical impacts of climate change wikipedia , lookup
Politics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate sensitivity wikipedia , lookup
Climate engineering wikipedia , lookup
Citizens' Climate Lobby wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on humans wikipedia , lookup
Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme wikipedia , lookup
Scientific opinion on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Global warming wikipedia , lookup
Public opinion on global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and poverty wikipedia , lookup
Surveys of scientists' views on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on Australia wikipedia , lookup
Climate change, industry and society wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Attribution of recent climate change wikipedia , lookup
IPCC Fourth Assessment Report wikipedia , lookup
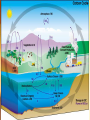
Climate Change Factors Lesson 6 Climate Change Factors • Climate Forcings – The initial drivers of a climate shift Climate feedbacks • The processes that change as a result of a change in forcing, and cause additional climate change. – A feedback that increases an initial warming is called a "positive feedback." A feedback that reduces an initial warming is a "negative feedback." Forcings Solar Irradiance. • The sun has a 11-year irradiance cycle that produces about 0.1% variation in output. Solar irradiance has been measured by satellite daily since the late 1970s, and this known solar cycle is incorporated into climate models. Aerosols, dust, smoke, and soot. • These can be produced by natural sources and human activity. They can also have very different effects on climate. • Sulphate aerosols, which result from burning coal, biomass, and volcanic eruptions, tend to cool the Earth. • Greenhouse gases such as CFC’s cause the Earth to become warmer. Feedbacks Clouds. • Clouds have an enormous impact on Earth's climate, • They reflect one third of the total amount of sunlight that hits the Earth's atmosphere back into space. Clouds • As the atmosphere warms, cloud patterns may change, altering the amount of sunlight absorbed by the Earth. Because clouds are such powerful climate actors, even small changes in average cloud amounts, locations, and type could speed warming, slow it, or even reverse it. Carbon cycle • Currently, natural processes remove about half of each year's human carbon dioxide emissions from the atmosphere, although this varies a bit year to year. Carbon is absorbed by land plant life. • There is also some evidence that the ability of the Earth’s ability to continue absorbing carbon may decline as the world warms, leading to faster accumulation in the atmosphere.. Melting Ice • "ice-albedo feedback." As the atmosphere warms, sea ice will melt. Ice is highly reflective, while the underlying ocean surface is far less reflective. The darker ocean will absorb more heat, getting warmer and making the Earth warmer overall. Watch An Inconvenient Truth You Tube Link to What can be done