* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Other Infectious Diseases
Cysticercosis wikipedia , lookup
Tuberculosis wikipedia , lookup
Chagas disease wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Neglected tropical diseases wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Meningococcal disease wikipedia , lookup
History of biological warfare wikipedia , lookup
Ebola virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Brucellosis wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Bioterrorism wikipedia , lookup
Trichinosis wikipedia , lookup
Whooping cough wikipedia , lookup
Onchocerciasis wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Coccidioidomycosis wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Neisseria meningitidis wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Leishmaniasis wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Eradication of infectious diseases wikipedia , lookup
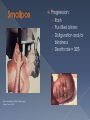
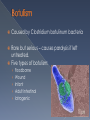
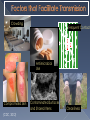
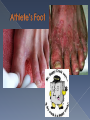
What disease killed 300-500 million people worldwide but has since been eradicated from the human population? Progression: › Rash › Pus-filled blisters › Disfiguration and/or blindness › Death rate = 30% Man with smallpox; Public Health Images Library. Source: CDC The first vaccine Edward Jenner 1749 - 1823 1967: WHO announces global smallpox eradication program. › Still 15 million new cases a year then 1977: Last reported naturally occurring case in Somalia. › Smallpox is the only disease totally eradicated in humans Ring around the rosy, A pocket full of posies, Ashes… Ashes, We all fall down! Written in London in 1665 Gangrene caused by plague 13 cases reported in Oregon (5 fatal) since 1970. Mostly spread from fleas of infected rodents. Caused by Clostridium botulinum bacteria Rare but serious – causes paralysis if left untreated. Five types of botulism: › › › › › Foodborne Wound Infant Adult intestinal Iatrogenic Symptoms include: › Double vision, blurred vision, drooping eyelids, slurred speech, difficulty swallowing, dry mouth, muscle weakness. Antitoxin is available for treatment Proper food handling › Especially in food preservation › Be wary of dented, bulging cans Botulism’s not all bad…. Flu seasons vary from year to year About 20% of US population infected every year › Higher among susceptible populations Three main types of flu virus: Types A, B & C › Type A causes the greatest morbidity and mortality Example: H1N1 (2009 Epidemic) Since the late 19th century, four occurrences of pandemics › 1889-1891; 1918-1920; 1957-1958; 1968-1969 2009; H1N1 › Was that the pandemic for our time?? Type A cycles every 50-100 years What’s different about Type A influenza? 20-33% world’s population is infected with TB › Majority of the above = “Dormant TB” Can be dormant for 30 years › Only 5-10% will become “active” TB Public.health.oregon.gov Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus Aureus › Staph bacteria resistant to certain antibiotics called beta-lactams. Often appears as pustule or boil › May think of a spider bite at first. HA-MRSA = Health care acquired › More serious and potentially deadly CA-MRSA = Community acquired › Anyone is at risk Crowding Frequent Contact Antimicrobial Use Compromised Skin (CDC, 2012) Contaminated Surfaces and Shared Items Cleanliness Newberg, Oregon… › High schooler spread MRSA through tattoos, several students infected. › Mainly spread through unclean needles. Ebola Flesh-eating disease Mad cow Kissing disease Giardia HAV U.S. Stats HBV HCV 25,000 new infections/yr 43,000 new infections/yr 17,000 new infections/yr Transmission Ingestion of fecal matter Contact w/ infectious body fluids Contact w/ infected blood Severity Usually no lasting damage, rarely fatal Most fully recover; Some develop liver disease; ~3,000 die / yr 60-70% develop chronic liver disease; 1-5% will die from liver cancer Vaccine? Vaccine available Vaccine available No vaccine Symptoms CDC, 2012 Fever, fatigue, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, joint pain, jaundice Gonorrhea Syphilis



























![Helicobacter Pylori Vaccine Development [Catherine Johnson]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008379278_1-060010de58f9bf0a5f198cab82e235c0-150x150.png)