* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Physics 517/617 Experiment 6A Digital Circuits
Time-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Flip-flop (electronics) wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Control system wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope history wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Analog-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
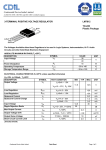
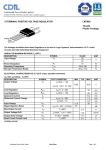
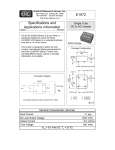
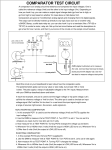
Physics 517/617 Experiment 6A Digital Circuits Basic Experiment - Physics 517/617 Almost all the circuits in this part of the course will be built using the "DIGI DESIGNER" and tested using a logic probe. You should become familiar with both of these tools before you start the lab. 1) Verify the truth table for a NAND Gate (7400 chip), NOR Gate (7402), AND (7408), OR Gate (7432), and Exclusive OR Gate (7486). Use the lamp switches on the DIGI designer to signal a high or low state. What is the output voltage of a high or low state? 2) Verify the truth table for the JK flipflop (74S112) including reset and clear options. 3) Using 3 J-K flipflops build a circuit that counts from zero to seven, i.e. 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 0, … Using the oscilloscope measure the maximum speed the counter can reliably work at. 4) The following is a design for a Flash ADC. For what ranges of Vin will A, B, and C be high and low. Design logic so the flash ADC will output the value Vin as a 2-bit digital number (5V/4bit*(21*D1+20*D0)). 5V Vin R LM311 C D1 R Logic B D0 R Voltage Vin > 3.57 2.5<Vin<3.75 1.25<Vin<2.5 Vin<1.25 D1 D0 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 A R 5) Build the circuit above to output A, B, and C. You don’t need to add the logic of part 4. Note: A comparitor converts a analog voltage into a digital pulse. For a comparator use LM311's. If the positive (+) terminal of the LM311 is at a higher voltage than the negative (-) terminal you get 5 volts output. Otherwise you get zero volts output. The 1K Ohm resistor is called a “pull up” resistor.