* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lab-3
Spectrum analyzer wikipedia , lookup
Chirp compression wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Spectral density wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Mechanical filter wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Electrostatic loudspeaker wikipedia , lookup
Transmission line loudspeaker wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Ringing artifacts wikipedia , lookup
Distributed element filter wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Analogue filter wikipedia , lookup
Utility frequency wikipedia , lookup
Audio crossover wikipedia , lookup
Chirp spectrum wikipedia , lookup
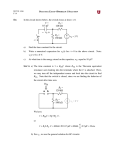
Filters • By combining resistor, capacitor, inductor in special ways we can design circuits that are capable of passing certain frequency while rejecting others. • Some example of filters are low pass filter, high pass filters and band pass filters. • Low pass filter circuits pass only the low frequencies but rejects high frequencies. Low pass filter • Combination of R and C. • It has a frequency sensitive voltage divider. • Frequency sensitive part comes from the C. • At high frequency capacitors reactance decreases. Output voltage decreases too. • At low frequency capacitor reactance increases. Output voltage increases too. Attenuation Vs Frequency • From the circuit we can find that • The magnitude or attenuation • When ω is 0, attenuation is 1 which means low frequency passes through the circuit. When ω is infinity, attenuation is 0, which means high frequency cannot pass the circuit. The cut-off frequency is the frequency at which attenuation is i.e. |Vout|= |Vin| At cutoff frequency • • • Attenuation in dB • • Attenuation is expressed in dB Decibel / non-decibel conversion • • Notice that when =0.707 (half power condition), AdB=-3dB Notice that at the points where dB values are minus are true attenuation; If dB value is positive can be considered as gain. Phase shift vs frequency • • • • • For any filter we should consider phase shift as well as the attenuation. Phase shift is a measurement to determine how much output signal has been shifted in phase related to the input voltage. Phase shift is As ω goes 0, phase shift goes 0° (i.e no phase shift). When ω goes to infinity phase shift goes to -90°. Phase shift also can be written in terms of cut off frequency: Where • Notice that when ω=ωc , phase shift is -45° Rectifier • • • • A step down transformer reduces the 120VAC to 12VAC Diodes passes only the positive portion of the signal. The filter capacitor smoothes the signal. 7805 outputs a regulated +5V 120VAC 7805 IC 5VDC