* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Signal-flow graph wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Solar micro-inverter wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Semiconductor device wikipedia , lookup
Network analysis (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
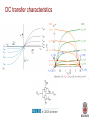
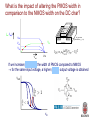
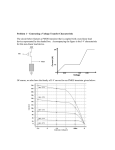
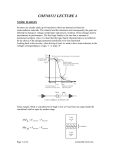
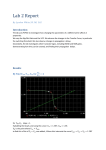
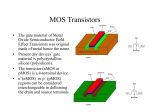
Design and Implementation of VLSI Systems (EN0160) Prof. Sherief Reda Division of Engineering, Brown University Spring 2007 [sources: Weste/Addison Wesley – Rabaey/Pearson] Summary of last lecture NMOS transistor PMOS transistor Summary of transistor ideal (Shockley) model polysilicon gate W tox n+ L n+ SiO2 gate oxide (good insulator, ox = 3.9) p-type body 0 Vgs Vt V I ds Vgs Vt ds Vds Vds Vdsat 2 2 V V Vds Vdsat gs t 2 for nMOS for pMOS cutoff linear saturation DC transfer characteristics PMOS on (linear), NMOS off • Vin = 0 Vin0 Idsn, |Idsp| Vin0 Vout VDD PMOS on (linear), NMOS on (saturation) • Vin = 0.2VDD Idsn, |Idsp| Vin1 Vin1 Vout VDD PMOS on (linear ~ sat) and NMOS (sat) • Vin = 0.4VDD Idsn, |Idsp| Vin2 Vin2 Vout VDD PMOS on (sat) NMOS on (linear) • Vin = 0.6VDD Idsn, |Idsp| Vin3 Vin3 Vout VDD PMOS on (off ~ linear) and NMOS on (linear) • Vin = 0.8VDD Vin4 Idsn, |Idsp| Vin4 Vout VDD NMOS on (linear) and PMOS cut off • Vin = VDD Vin0 Idsn, |Idsp| Vin5 Vin1 Vin2 Vin3 Vin4 Vout VDD Summary of voltage transfer function A B C D E Noise margins CMOS inverter noise margins desired regions of operation What is the impact of altering the PMOS width in comparison to the NMOS width on the DC char? polysilicon gate Idsn, |Idsp| W tox Vin3 n+ Vin3 Vin3 L n+ SiO2 gate oxide (good insulator, ox = 3.9) p-type body Vin3 Vout VDD If we increase (decrease) the width of PMOS compared to NMOS for the same input voltage, a higher (lower) output voltage is obtained V out V in Impact of skewing transistor sizes on inverter noise margins Increasing (decreasing) PMOS width to NMOS width increases (decreases) the low noise margin and decreases (increases) the high noise margin Pass transistor DC characteristics As the source can rise to within a threshold voltage of the gate, the output of several transistors in series is no more degraded than that of a single transistor Summary • Today – Covered DC transfer characteristics • Next time – Transistor non-ideal behaviour