* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sunni vs. Shia - Moore Middle School PTSA
The Jewel of Medina wikipedia , lookup
Shia–Sunni relations wikipedia , lookup
Islam and secularism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and modernity wikipedia , lookup
Islamic democracy wikipedia , lookup
Salafi jihadism wikipedia , lookup
Imamate (Twelver doctrine) wikipedia , lookup
Satanic Verses wikipedia , lookup
Islamic culture wikipedia , lookup
History of Nizari Ismailism wikipedia , lookup
Historicity of Muhammad wikipedia , lookup
History of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Sources of sharia wikipedia , lookup
Husayn ibn Ali wikipedia , lookup
Islam and war wikipedia , lookup
Sectarian violence in Pakistan wikipedia , lookup
Islam and other religions wikipedia , lookup
Political aspects of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Succession to Muhammad wikipedia , lookup
Anti-Shi'ism wikipedia , lookup
Usul Fiqh in Ja'fari school wikipedia , lookup
Imamah (Shia) wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Twelver Shia Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islamic schools and branches wikipedia , lookup
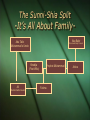
Sunni vs. Shia Deconstructing Islam for the Classroom What Do We Know about Sunni and Shia Islam? Images of Sunni and Shia Violence Islam-The Big Picture The Prophet Muhammad (pbuh)receives the revelation of the Qu’ran in 610 612 Prophet Muhammad (phuh)begins preaching The Qu’ran holds 114 chapters or “surahs”. It took 21 years for the Qu’ran to be fully revealed. The Qu’ran’s surahs are not ordered chronologically but according to lengthlongest to shortest. Five Pillars of Islam Shahada- the Declaration of Faith. One becomes a Muslim by saying the following with conviction and belief: “La ilaha illa Allah, Muhammadur rasoolu Allah.” “There is no god but Allah and Muhammad is his messenger.” Salat- Prayer. Muslims are to pray five times a day in the direction of the Kaabah in Mecca. Prayers are performed at dawn, noon, midafternoon, sunset, and night. Five Pillars of Islam Zakat- Alms-giving to benefit the poor and needy, required every year (normally at the end of Ramadam). 2.5% of wealth, volunteer time can count towards this. Sawm- Fasting. For the entire month of Ramadan (on the lunar calendar) believers abstain from food, drink and impure thought and deeds during the daylight hours. The month commemorates the first revelation of the Qu’ran and is seen as spiritually purifying. The end of Ramadan is a holiday, Eid al-Fitr Feast of Breaking the Fast. Five Pillars of Islam Hajj- The Pilgramage to Mecca during the month of Dhu al-Hijjah. If able every Muslim is expected to make the Hajj at least once in their lifetime, if unable many sponsor someone to go in their place. It is common for a village to pull together their money to pay the way for one individual to go on behalf of all. The end of Dhu al-Hijjah is another holiday, Eid al-Aida, Feast of the Sacrifice. Additional Component Jihad- Important concept in both Sunni and Shia Islam, signifies a struggle. Two types, the struggle within (which the Qu’ran deals mainly with), and the struggle (wars of religion) without. Shia consider the inner Jihad an essential element of the faith. Jihad is often misused in terminology and in its purpose. Terrorist group AlQaida is a Sunni organization. Definitions PBUH- Stands for “Peace Be Upon Him” and is commonly said or written after using the Prophet Muhammad’s name by Muslims. Qu’ran- the Holy book of the Islamic faith, the word means “recitation”. Many believers, as well as Muhammad himself, were illiterate and learned all teachings orally. Surah- a chapter within the Qu’ran Islam- means “surrender” Muslim- means “one who surrenders” Ummah- the religious community Ahl al-Kitab- “People of the Book”, refers to Jews and Christians or ‘people of an earlier revelation’ The Sunni-Shia Split -It’s All About FamilyMuhammad and Khadija are credited with having several daughters, although the parentage of them is questioned by scholars; they may have been adopted by Muhammad rather than sired by him. Uthman (the 3rd Caliph) was married to one of these daughters, Umm Kulthum bint Muhammad. However, historically these daughters have been marginalized, most likely because they did not bear any surviving children or survive their father. For the purposes of this presentation, all family relations have been simplified, thus we can state that Fatima was the only surviving daughter of Muhammad. Khadija First Wife Prophet Muhammad Fatima The Sunni-Shia Split -It’s All About FamilyAbu Bakr Abu Talib Muhammad’s Uncle Friend and Early Convert Khadija (First Wife) Ali Muhammad’s Cousin Prophet Muhammad Fatima Aisha The Sunni-Shia Split -It’s All About Family- Hassan 2nd Imam Fatima Ali 1st Imam Hussein 3rd Imam Zaynab Ali Zain Al-Abideen 4th Imam All Other Imams Descend from this Line. Umm Al-Kaltum Muhammad’s Succession 632- Muhammad dies, leaving no confirmed successor* Disagreement among clans on who will lead the faith- bloodline (Ali) or the one most capable The Ummah (the Islamic community) elects Muhammad’s father-in-law (through his wife Aisha) Abu Bakr to lead the faith. He becomes the first Caliph - the leader of the Ummah. The Rashidun (632-661) The Rule of the Four Righted Guided Caliphs Name Ruled Died Known For Abu Bakr 1st Caliph 632-634 elected Natural causes, appointed his successor Quelled rebellion and united Arabia Umar ibn alKhattab 2nd Caliph 634-644 appointed Stabbed in a Medina mosque by a POW with a personal grudge. Wars of expansion (power not religion but religion followed) to the greater Middle East Uthman ibn Affan 3rd Caliph 644-656 elected Assassinated by those from the elite of Medina over the rise of status and power of the Umayyad clan. Expanded the empire to North Africa and Central Asia- but with much political cost. Standardized the Qu’ran. Ali ibn Abu Talib 4th Caliph/1st Imam 656-661 elected Assassinated by Kharajiites, a group of dissenters to Ali’s rule Ruled during the first Fitnah (civil war). His place in history is denoted more for who he was rather than what he did. First Fitnah A 5 Year Civil War that lasted through Ali’s Reign Angered over Ali’s reluctance to seek revenge in the death of Uthman, Aisha and her kinsman lead a revolt against Ali in the Battle of the Camel, which was lost by the rebels. Ali’s rule was not supported in Syria (where Uthman had appointed members of the Umayyad clan in power). Mu’awiya, governor of Syria, also wanted revenge for Uthman’s death. The Battle of Siffin (657) ended in arbitration between the two sides, which seriously hurt Ali politically. A Community Divided The Shia (followers of Ali) had been supporting Ali as the rightful head of the Islamic faith since the death of Muhammad. Now as Ali was being persecuted politically, the idea of being unfairly treated was being ingrained in the Shia psyche. As Ali was not actively seeking retribution for Uthman’s death, the Ummah was growing more and more discontent with the Caliph, garnering more support for challengers to the Caliphate like Mu’awiya. The Ummah was also horrified by the infighting between those that had once been a part of Muhammad’s inner circle, the community wanted a strong leader, not only for their protection but for the preservation of the faith. The true split in Islam came with the death of Ali. The Shia, who supported Ali went one way, and the Sunni, who followed Mu’awiya I (who declared himself Caliph and began the Umayyad dynasty) went the other. Second Fitnah Mu’awiya I had managed to reconsolidate the Ummah, although in order to keep the community intact long-term, a new style of government closer to a monarchy than of an Arab Chieftain was needed. Mu’awiya arranged for his son Yezid to succeed him. Outraged at the choice of succession, Hussein (the son of Ali) and his followers demanded their rights to the Caliphate, which culminates in the Battle of Karbala in 680. The Battle of Karbala and its outcomes Supporters of Hussein ibn Ali against Yazid I, the Umayyad caliph. Horribly outnumbered: under 100 vs. 4000+ Results- all men were massacred, women and childern in capitivity and made to march to Damascus, including Hussein’s sister Zaynab The Martyrdom of Hussein is celebrated by Shia, this day is called Ashura. Sunni and Shia Today Population statistics (Sunni 90%, Shia 10%) Cult of Martyrdom- the 12 Imams Concept of the Mahdi Areas of the World where conflict between the two exist. Iraq and Bahrain Sunni and Shia Today Concealing Faith for Self Protection Temporary Marriages Frequency of Prayer Holidays Sunni: Eid al-Adha, Eid al-Fitr Shia: Eid al-Adha, Eid al-Fitr, Ashura Ashura- a day of mourning. Men would beat their chests, and cut their bodies with knives. As most religious elite ban the cutting practice it still happens, they encourage the Shia to donate blood instead to commemorate the blood spilled at the battle of Karbala. Holy Places Sunni: Mecca, Medina, Jerusalem Shia: Mecca, Medina, Jerusalem, Najaf (Site of Ali’s Tomb), Karbala Recap Sunni The Sunni branch believes that the first four caliphs--Mohammed's successors-rightfully took his place as the leaders of Muslims. They recognize the heirs of the four caliphs as legitimate religious leaders. These heirs ruled continuously in the Arab world until the break-up of the Ottoman Empire following the end of the First World War. Recap Shia Shiites, in contrast, believe that only the heirs of the fourth caliph, Ali, are the legitimate successors of Mohammed. In 931 the Twelfth Imam disappeared. This was a seminal event in the history of Shiite Muslims. Recap Shia According to R. Scott Appleby, a professor of history at the University of Notre Dame,"Shiite Muslims, who are concentrated in Iran, Iraq, and Lebanon, [believe they] had suffered the loss of divinely guided political leadership" at the time of the Imam's disappearance. Recap Shia Not until the ascendancy of Ayatollah Ruhollah Khomeini in 1978" did they believe that they had once again begun to live under the authority of a legitimate religious figure. Loss of a Leader for Sunni Muslims, approximately 90 percent of the Muslim world, the loss of the caliphate after World War I was devastating in light of the hitherto continuous historic presence of the caliph, the guardian of Islamic law and the Islamic state. Osama Bin Laden Osama bin Laden is a Sunni Muslim. To him the end of the reign of the caliphs in the 1920s was catastrophic, as he made clear in a videotape made after 9-11. On the tape, broadcast by AlJazeera on October 7, 2001, he proclaimed Taliban Radical Muslim group Based in Afghanistan Osama Bin Laden Quote :"What America is tasting now is only a copy of what we have tasted. ... Our Islamic nation has been tasting the same for more [than] eighty years, of humiliation and disgrace, its sons killed and their blood spilled, its sanctities desecrated." 9/11 The Taliban came into conflict with the United States. Investigation on the September 11, 2001, terrorist attacks on New York City and Washington D.C. Led to terrorist leaser Osama Bin Laden. 9/11 Osama bin Laden led a terrorist network called Al Qaeda network which was based in Afghanistan. U.S and British forces attacked Taliban and Al Qaeda targets and toppled Afghanistan’s Taliban government. Pakistan Believed to work with terrorist groups and to have been hiding bin Laden. Bin Laden was recently found and killed by a U.S. special operations group. Thank you for Coming! All of the Powerpoint presentation and handouts for this presentation can be found on our website: www.mec.utah.edu/outreach





















































![Quiz About [Your Topic]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008403451_1-2c0c5d99550f956fde8d6a5d53519c7c-150x150.png)