* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Earth`s Structure
Survey
Document related concepts
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Supercontinent wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
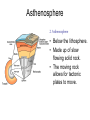
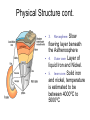
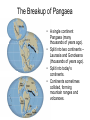
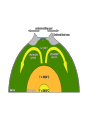
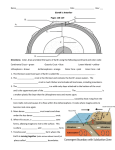
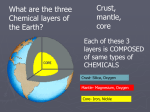
Earth’s Structure The layers of Earth • Earth is divided into 3 layers based on chemical composition. 1) Core: Dense metallic center, made up of mainly metal iron. 2) Mantle: Liquid middle layer made up of silicon, oxygen and magnesium. 3) Crust: The solid outer layer made up of silicon, oxygen and aluminum. Continental and Oceanic Crust • There are two types of crust: 1. Continental: is thicker 2. Oceanic: is thinner and heavier. • Compared to the other layers, both types of crust are rocky, thin and fractured. The Physical Structure of Earth • Earth is divided into five layers based on physical properties. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Lithosphere Asthenosphere Mesosphere Outer core Inner core Lithosphere 1. Lithosphere: cool rigid layer, made up of the crust and upper layer of the mantle. Lithosphere is divided into pieces called tectonic plates. Asthenosphere 2. Asthenosphere • Below the lithosphere. • Made up of slow flowing solid rock. • The moving rock allows for tectonic plates to move. Physical Structure cont. • 3. Mesosphere: Slow flowing layer beneath the Asthenosphere • 4. Outer core: Layer of liquid Iron and Nickel. • 5. Inner core: Solid iron and nickel, temperature is estimated to be between 4000ºC to 5000ºC Mapping Earth’s Interior • How can we know so much about Earth’s interior if no one has ever drilled through the crust? • Earthquakes produce seismic waves, and travel thru materials at different speeds. • Scientists use these waves to determine the density of each of Earth's layers Continental Drift • In the 1900’s,Scientist Alfred Wagner, viewed the continents as puzzle pieces. • Had a hypothesis that our continents used to be one large continent. • He named his hypothesis the Continental Drift Theory. Evidence for Continental Drift • Fossils of same plant can be found on continents that are far from each other. • Location of mountain ranges with similar rocks show a pattern. The Breakup of Pangaea • A single continent Pangaea (many thousands of years ago). • Split into two continents – Laurasia and Gondwana (thousands of years ago). • Split into today's continents. • Continents sometimes collided, forming mountain ranges and volcanoes. Sea-Floor Spreading. • When Wagner introduced his hypothesis, many scientists did not accept it because the strength needed to move Earth’s crust seemed impossible. • In the 1960’s Scientist studying the ocean floor discovered identical patterns of magnetism on both sides of the mid ocean ridge. • This was proof that continental drift was possible. Sea-Floor Spreading cont. • At a mid-ocean ridge, magma rises through fractures in the sea floor. • As the magma cools it forms new sea floor. • As this continues to happen, new floor is made and older floor is pushed away from the fracture. • Sea-floor spreading was proven to cause continents to move.