* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download a Introduction to Geology
Survey
Document related concepts
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
History of climate change science wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
Meteorology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geodesy wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
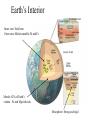
Chaos Theory How long is the coastline of the United States? Depends on the length of the ruler used… Chaos Theory Weather models….. Only as good as the number of variables inputted…. Butterfly Effect: In a remote part of the Amazon jungle, a butterfly alights upon a tree limb. The butterfly rests there for a moment, and then flutters its wings. A week later, the weather in New York is affected. No instruments presently known could measure the perturbation, but it happens. It is called “the Butterfly Effect.” This strange effect promotes the idea that in a chaotic system, a very small change to that system applied at a certain point in time makes the future change in a very dramatic way. Something as small as a butterfly flapping its wings now might affect the weather system on a global scale six months in the future. Earth systems are all interrelated, and small variables can cause significant changes. Catastrophism All the Earth’s great landforms are the result of great catastrophes. Grand Canyon Edinburgh Castle, Scotland Arthur’s Seat James Hutton Hutton’s Section Uniformitarianism The present is the key to the past Present day processes Time Jan 1 Origin of the Earth: January 1 Oldest known rocks: Early March Living things appear in oceans: May Land plants and organisms: Late November Dinosaurs: Dominant from mid-December to the 26th On the 31st: Humans appear: 11:49pm End of last ice age: 11:58:17pm Fall of Roman Empire: 11:59:49pm Columbus: 11:59:57pm World War I: 11:59:59.4pm Y2K: 11:59:59.9993pm Every real year equates to 1/7000 of a second Dec 31 Earth’s Interior Inner core: Solid iron Outer core: Molten metallic Ni and Fe Mantle: 82% of Earth’s volume. Fe and Mg-rich rock. Mesosphere: Strong and rigid Tectonic Plates Crust + Rigid upper mantle (lithosphere)