* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Carbon Cycle and Global Warming
Survey
Document related concepts
Solar radiation management wikipedia , lookup
Iron fertilization wikipedia , lookup
IPCC Fourth Assessment Report wikipedia , lookup
Citizens' Climate Lobby wikipedia , lookup
Carbon pricing in Australia wikipedia , lookup
Mitigation of global warming in Australia wikipedia , lookup
Politics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Reforestation wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Climate change feedback wikipedia , lookup
Carbon sequestration wikipedia , lookup
Climate-friendly gardening wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
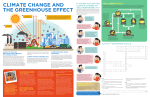
Science 10 O2 Amount of matter on Earth is constant with the exception of a few asteroids NEED to recycle matter in order to maintain our planet There are many cycles: carbon, nitrogen, and water are examples. Organic Matter: substances which contain atoms of carbon and hydrogen, and often nitrogen and oxygen as well. Ex: proteins, sugars, fats Inorganic Matter: substances that do not contain carbon AND hydrogen atoms. Ex: water, carbon dioxide, ammonia Matter is recycled by: • Eating food (which is organic matter) and through death. • Decomposers are key in this recycling cycle. Carbon is the key element for living things. Each year, 50-70 billion tonnes of carbon are recycled. Photosynthesis: plants use light energy to combine carbon dioxide and water to make glucose (sugar) and oxygen Respiration: living things use oxygen to break down sugars and release water and carbon dioxide as the sugars are broken down. What do you notice about these two processes? A lot of carbon is being continuously recycled by organisms, but a large amount of inorganic carbon is also stored in three major areas: • The atmosphere – smallest amount • The oceans – dissolved CO2 for algae and plants • The earth’s crust – largest amount of storage and can remain there for millions of years • How do you think it gets released? Organic carbon storage: in the bodies of living things. When living things die, decomposers return organic carbon to the cycle in an inorganic form. Exception: large amounts of organic carbons are stored in bogs. • Little oxygen so decomposition is very slow • Carbon remains locked in peat for many years. • Compression of many peat layers = coal/fossil fuels http://www.windows2universe.org/earth/climate/carbon_cycle.html http://www.biology.ualberta.ca/facilities/multimedia/uploads/alberta/CarbonCycle .html Humans have sped up the release of organic carbon through the mining and burning of fossil fuels, and through burning forests What does this contribute to? Global warming is the increase in the average temperature of Earth's nearsurface air and oceans since the mid-20th century and its projected continuation. The atmosphere is made up of layers of gases When the sun’s heat warms the surface of the Earth, some of it is reflected back into the atmosphere The layers of gases can prevent the heat from the Earth to reflect back from its surface to space, much like a greenhouse. water vapour - occurs naturally in the atmosphere. carbon dioxide - produced naturally when people and animals breathe and from burning fossil fuels Methane- comes from cattle as they digest their food. The gas also comes from fields where rice is grown in paddy fields. nitrous oxide - when plants die and rot, nitrous oxide is produced. Ozone- occurs naturally in the atmosphere. CFC’s Planet becomes warmer: • Weather patterns will change (depending on area) • Sea levels will rise • Animals will be endangered • Humans will be endangered http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5zLuqSYF68E A carbon footprint is "the total set of greenhouse gas emissions caused by an organization, event, product or person.“ Greenhouse gases can be emitted through transport, land clearance, and the production and consumption of food, fuels, manufactured goods, materials, wood, roads, buildings, and services. Solar variation theory The warming is within the range of natural variation and needs no particular explanation. The warming is a consequence of coming out of a prior cool period — the Little Ice Age — and needs no other explanation. The warming trend itself has not been clearly established, and therefore does not need any explanation. Complete the worksheet on the carbon cycle using pgs 26-29 Calculate your carbon footprint using the handout provided and list 3 ways you can reduce your personal carbon footprint