* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2.02 Supply and Demand
Survey
Document related concepts
Supply chain management wikipedia , lookup
Yield management wikipedia , lookup
Grey market wikipedia , lookup
Revenue management wikipedia , lookup
Natural gas prices wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Pricing science wikipedia , lookup
Gasoline and diesel usage and pricing wikipedia , lookup
Service parts pricing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Dumping (pricing policy) wikipedia , lookup
Pricing strategies wikipedia , lookup
Price discrimination wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
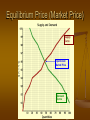
2.02 Supply and Demand 02.00 Understand Economics and Economic Systems 02.02 Interpret supply and demand graphs Marketplace In a free market, consumers determine the demand of a product. Entrepreneurs see the demand and make more of the product. More supply causes the price to decrease as the demand is fulfilled. Supply Defined How much of a good or service a producer is willing and able to produce at different prices. Supply is produced by the businesses in hopes of making money. Demand Defined An individual’s need or desire for a good or service at a given price. Individuals are willing to consume more of product or service at a lower price. When the demand is high, competitors see opportunity in the market. Supply and Demand Graphs People draw supply and demand graphs so that they can easily see the relationship between the supply and the demand. A supply and demand graph is a visual representation of supply and demand. The graph shows changes in a product’s demand or supply. The graph can help predict the performance of the product over time. When Supply and Demand Meet The point at which the supply and demand curve meet is known as the equilibrium price and quantity. When the price is above the equilibrium price, fewer people are willing to buy—the price is too high. When the price is below equilibrium price, many people are willing to buy a lot of the product—the price is too low. Suppliers may not be able to make enough money to cover costs. Equilibrium Price (Market Price) Supply Curve Equilibrium/ Market Price Demand Curve Prices tell businesses what to produce The prices of goods and services dictate what products are developed, made, improved or modified. When the price is high, demand falls and businesses produce fewer goods. When the price is low, demand rises and businesses produce more goods to meet the demand. Competition is sparked Sellers compete to make a profit If a person sees that they can meet a need or a want, they enter the marketplace They compete with other businesses already meeting the need or want. OR They make a new product and competition follows when others enter the marketplace. The Profit Motive People and businesses enter the marketplace in hopes of making a profit (money). This “profit motive” encourages people to enter the marketplace. This hope of making a profit is the reward for people who take risks by entering the marketplace.