* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Survey
Document related concepts
Human nature wikipedia , lookup
American anthropology wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Social Bonding and Nurture Kinship wikipedia , lookup
Cultural ecology wikipedia , lookup
Marx's theory of human nature wikipedia , lookup
Social anthropology wikipedia , lookup
History of anthropometry wikipedia , lookup
Cultural anthropology wikipedia , lookup
Craniometry wikipedia , lookup
Human vestigiality wikipedia , lookup
Human variability wikipedia , lookup
Aquatic ape hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Discovery of human antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Human evolutionary genetics wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary origin of religions wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
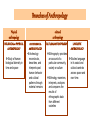
Anthropology The study of the human species and its immediate ancestors Studies man from a holistic point of view: • its culture as well as its origins and development as a human species. Discuss with your neighbour? 1) What does it mean to be human? 2)How are human beings unique? Anthropology • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=p7p_whtOtQ&feature=related Branches of Anthropology Physical anthropology BIOLOGICAL or PHYSICAL ANTRHOPOLOGY Study of human biological diversity in time and space cultural anthropology ARCHEOLOGICAL ANTRHOPOLOGY Archeology reconstructs, describes, and interprets past human behavior and cultural patterns through material remains CULTURAL ANTRHOPOLOGY LINGUISTIC ANTRHOPOLOGY Ethnography provides an account of a Studies language particular community, in its social and society or culture cultural contexts across space and over time. Ethnology examines, interprets, analyzes and compares the results of ethnographic data from different societies Let’s Check out Physical Anthropology • • • • What makes us human? How are we different from other species? What is the origin of the human species? What are the similarities and differences among human beings today? Let’s Meet Some Physical Anthropologist! Raymond Dart • Anthropology teacher in South Africa • In 1924 Discovered skull and fossilized brain of human child that lived three million years ago • He named the species AUSTRALOPITHECUS AFRICANUS Louis and Mary Leakey • They were searching for evidence of human ancestors in Tanzania in July of 1959 • They found a complete fossil skull • Important in establishing that the earliest human beings lived in Africa Donald Johanson • Digging in Ethiopia in 1974 • Found 40% of a skeleton that he named LUCY • First early skeleton of its type that could be reconstructed Jane Goodall • In the 1960’s was one of the first to study the behaviour of chimpanzees at close quarters • First to observe chimps making and using simple tools ( an activity thought to be uniquely human) Charles Darwin The Story of Creation Genesis 1:1-5, 20-26 In the beginning God created the heavens and the earth…God said “Let there be light,” and there was light. God called the light “day” and the darkness “night”. Together these made up one day. And God said, “Let the waters swarm with fish and other life. Let the skies be filled with birds of every kind.” And God said, “let the earth bring forth every kind of animal – livestock, small animals, and wildlife.” Then God said, “let us make people, in our image, to be life ourselves. They will be masters over all life –the fist in the sea, the birds in the sky, and all the livestock, wild animals and small animals. *NOTE: This was all said to have occurred in 6 days, the length of which is unclear ACTIVITY TIME • Froogliooops – Claws, language, fur • Barachooks –Fangs, perfect sight, can breath underwater • Weebers – Tall, Webbed feet, wings • Snilleywits – Small, no limbs, can breath underwater • Traloopos- Tail, great sense of smell, very tall Will you survive? Scenario #1: A predator came to town today! You can only survive if you hide in the lake, fly away or fight back if you have claws. Scenario #2: A huge storm is coming! You need shelter. You will only survive if you are small enough to fit in a hole underground, you can claw yourself a deeper hole, or you can look for a clear dry place to stay. • Scenario #3 – You are starving and need food. You will only survive if you can use your claws kill for food, or use your fangs to eat. • Scenario #4 – Your species is fighting! You will only survive if you can communicate with one another and share ideas. THEORY OF EVOLUTION THROUGH NATURAL SELECTION Charles Darwin’s Origin of the Species 1859 • Starts with the assumption that variations within species do happen but in tiny bits of expression. • The variations were carried by genes that formed part of the population’s gene pool. • Some of these variations allow organisms to become better adapted to the environment while others did not. • In the process of coping with survival, that variations that allowed greater adaptation of organisms to the environment were preserved in the gene pool and assured of better and greater chances for inheritance. • The species that inherited these “strong variants” survived and reproduced its kind. • The others died and became extinct. Ideas Behind Darwin’s Theory of Evolution 1) Overpopulation 2) Struggle for Existence 3) Variations 4) Survival of the Fittest 5) Inheritance of Variations The Evolution of Humans • Handouts – “The evolution of Humans” – “How did the human species develop?” – Skull worksheet – Figure 2.2 – “Distinguishing Apes From Humans” – “The Differences between Humans and Hominids” Human Diversity Primates vs Humans • Humans belong to the biological group called primates and are the highest order of mammals • May have a common ancestor • Genetic makeup of primates and humans varies by only 1-2 percent • We share many physical and some social characteristics That’s why physical anthropologist study primates! For clues on the evolution of humans Humans & Primates shared features • • • • • • Opposable thumbs Three dimensional(binocular) vision Highly developed brain Offspring dependent on adults for a long time Depend on the group for survival-social creatures Share a capacity for aggression and defense Unique Human characteristics • Bipedalism: walk upright over long distances • Ability to communicate complex and abstract ideas through language Becoming human • 3 anthropological hypothesis: 1)Aggressive warlike traits encouraged humans to develop tools and weapons (killing pary and enemies) 2) Language Development: Development of effective communication needed when hunting in groups combined with tool production 3) Social skills: human ability to get along in groups were crucial in the development of their ability to think(tool-hunting-language connection is only a consequence) Activity • Read” Human Diversity: Myth or reality” on page 22 and answer both questions in class.