* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download B - Sewanhaka Central High School District
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Dictyostelium discoideum wikipedia , lookup
Chimera (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Precambrian body plans wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic resistance to malaria wikipedia , lookup
Artificial cell wikipedia , lookup
Symbiogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal lineage marker wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to genetics wikipedia , lookup
Human embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Sexual reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell (biology) wikipedia , lookup
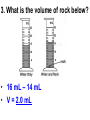
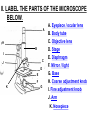
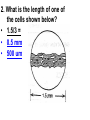
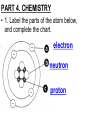
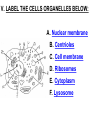
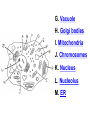
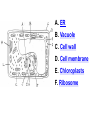
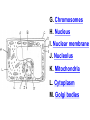
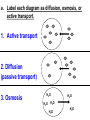
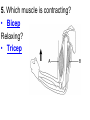
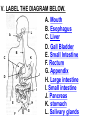
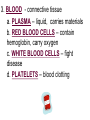
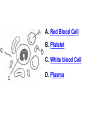
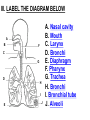
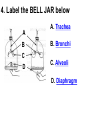
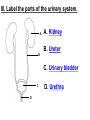
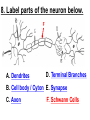
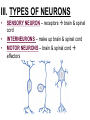
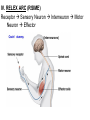
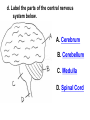
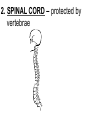
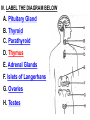
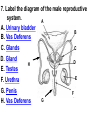
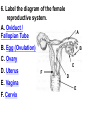
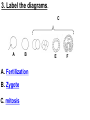
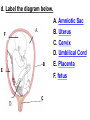
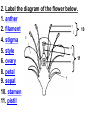
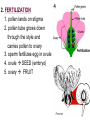
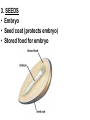
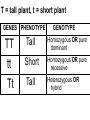
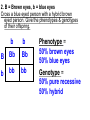
PART 1. SCIENTIFIC METHOD I. STEPS 1. PROBLEM - always in the form of a QUESTION 2. GATHER INFORMATION 3. HYPOTHESIS – EDUCATED GUESS 4. EXPERIMENT – test hypothesis 5. OBSERVATIONS - analyze data, charts, graphs… 6. CONCLUSION - is your hypothesis right or wrong? 7. Repeat II. EXPERIMENT. Example: A student set up the experiment shown to learn about plant growth. The student added a different amount of water to 4 identical containers, each containing 4 seeds in 100 cubic centimeters of soil. All of the containers were placed in the same sunny location. The height of the plants were measured and recorded for 5 weeks. a. State a hypothesis for this experiment. • I believe that the plants getting the most water will grow the most. b. Independent variable = • WATER c. Dependent variable = • HEIGHT d. Control Group = • Seeds that do not receive water e. Identify 3 factors that must remain constant. • Amount of soil, amount of sunlight, location, # of seeds, types of seeds… f. What can be done to make the experiment more valid? • Repeat, increase sample size, use only one variable PART 2. MEASUREMENT I. LENGTH – meter 1. What is the length of the tadpole at the right? • • • • In centimeters= 3.1 cm In millimeters = 31 mm II. MASS – • the amount of matter in an object 1. What instrument is being used to measure the mass of the object at the right? • TRIPLE BEAM BALANCE 2. What is the mass of the object? • 175.0 gm III. VOLUME – • The amount of space an object takes up 1. Calculate the volume of the block below. Show all work in the work space below. • V=lxw xh • V = 2.4 cm x 4.2 cm x 5.3 cm • V = 53.4 cm3 2. What is the name of the instrument below? • GRADUATED CYLINDER 3. What is the volume of rock below? • 16 mL – 14 mL • V = 2.0 mL IV. REVIEW QUESTIONS 1. What is the temperature shown in the thermometer shown at the right? • 25°C 2. Convert the following measurements: a. 2.45 cm = ?km k 0.0000245 km h Left d Base ( meter, liter, gram) m b. 5.46 L = ?mL 5460.0 mL Right d c m PART 3. MICROSCOPE I. PARTS & FUNCTIONS: 1. eyepiece/ocular lens – lens that you look through 2. body tube – connects objective & eyepiece 3. stage – holds the slide 4. coarse adjustment knob – focusing under low power. 5. mirror/light source – provides light 6. fine adjustment knob – focusing for high power 7. base – structure that supports microscope 8. objective lens – lenses that magnify 9. diaphragm – controls amount of light 10. arm – supports body tube II. LABEL THE PARTS OF THE MICROSCOPE BELOW. A H B I C J D E F K G A. Eyepiece / ocular lens B. Body tube C. Objective lens D. Stage E. Diaphragm F. Mirror / light G. Base H. Coarse adjustment knob I. Fine adjustment knob J. Arm K. Nosepiece III. USING THE MICROSCOPE 1. What would happen if you used the coarse adjustment under high power? • The lens and the slide may break! 2. When you observe a specimen using a microscope, how does the specimen appear? • Upside down and backwards 3. When you move the slide in any direction, how does the specimen on the slide appear to move? • In the opposite direction 4. Which objective lens allows you to observe LARGER field of view? • Low power 5. Calculate the total magnification: Eyepiece = 15x, Objective = 5x • Total Mag = 75x 6. What is the student in the picture at the right preparing? • Wet mount 7. Why should the student make sure the cover slip is lowered at an angle? • To prevent air bubbles from forming IV. MEASURING WITH THE MICROSCOPE 1. What is the diameter of the field of view shown below? • 3.6 mm • 3600 um 2. What is the length of one of the cells shown below? • 1.5/3 = • 0.5 mm • 500 um 3. Determine the lengths of the objects in the microscopes field of view below? a. 0.8 mm 800 um 4. How many micrometers make up one millimeter? • 1000 um PART 4. CHEMISTRY • 1. Label the parts of the atom below, and complete the chart. electron neutron proton CHARGE SUBATOMIC LOCATION PARTICLE Electron Outside nucleus Negative (electron cloud) Neutron Nucleus No charge Proton Nucleus positive • 2. DEFINE THE FOLLOWING TERMS: • a. ELEMENT – • Simple substance that cannot be broken down into something more simple • b. COMPOUND – • 2 or more elements chemically combined • c. MIXTURE – • 2 or more substances physically combined • 3. Identify each property below as a physical or chemical property. • a. Burning: • chemical • b. color: • physical • c. phase (solid, liquid, gas): • physical • 4. Identify each change below as a physical or chemical change. • • • • • • • • a. Ripping paper: physical b. burning paper: chemical c. melting: physical d. baking a cake chemical • 5. Fill in the chart below describing phases of matter: SPEED PHASE OF MATTER a. SOLID POSITION OF PARTICLES Tightly packed b. LIQUID Sliding past each A little faster other Very far apart Very fast c. GAS vibrating • 6. For each phase change below, identify how the material is changing, and whether heat is being absorbed or released. • • • • • • • • a. melting: S L, heat absorbed b. freezing L S, heat released c. evaporation L G, heat absorbed d. condensation G L, Heat released 7. Identify 4 properties of metals: • have luster • Ductile • Malleable • Good conductors of heat and electricity 8. Identify 3 properties of nonmetals: • brittle • Dull (not shiny) • Poor conductors of heat and electricity 9. Identify the parts of the periodic table being described below: • • • • • • • • • • • • a. Rows: periods b. Elements to left of zig zag line: metals c. Columns: Groups/families e. Group18: Noble gases f. On zig zag line: Semi-metals/metalloids g: Elements to right of zig zag line: nonmetals • 10. Atomic number: • # of protons • 11. Mass number: • # of protons + # of neutrons • Atomic mass rounded to nearest whole number 12. The diagram below represents n element from the period table. • • • • • • • • • • Atomic #: 14 Atomic Mass = 28.0855 Mass # = 28 # of protons in each atom of this element = 14 # of neutrons 28-14 = 14 • 13. On the pH scale below label which section refers to acids, bases, and which pH is considered neutral. base acids neutral PART 5. CELLS I. CELL THEORY 1. Who developed the cell theory? • • • • a. Hooke = cork under named what he saw “cells” b. Schleiden = all plants are made of cells c. Schwann = all animals are made of cells d. Virchow = all cells come from other cells 2. a. List the parts of the CELL THEORY below. • Cells are the basic unit of structure for all living things. • Cells are the basic unit of function for all living things. • All cells come from pre-existing cells. II. CELL ORGANELLES 1. Cell membrane – semipermeable 2. Nucleus – control center a. Nuclear membrane – surrounds nucleus b. Nucleolus – produces ribosomes c. Chromosomes – genetic material 3. Cytoplasm – jelly-like materials, holds all organelles 4. Mitchondria – produces energy (by respiration) 5. Endoplasmic Reticulum –tunnels in the cytoplasm (transport) 6. Vacuoles – storage 7. Ribosomes – produce proteins 8. Golgi bodies – packages and ships 1. Cell Wall – outer wall made of cellulose, protects, gives plant cell shape 2. Chloroplasts – carry out photosynthesis, contain chlorophyll (absorbs light) 1. Lysosomes – contain enzymes that break down/digest materials 2. Centrioles – aid in cell division V. LABEL THE CELLS ORGANELLES BELOW: A. Nuclear membrane B. Centrioles C. Cell membrane D. Ribosomes E. Cytoplasm F. Lysosome G. Vacuole H. Golgi bodies I. Mitochondria J. Chromosomes K. Nucleus L. Nucleolus M. ER A. ER B. Vacuole C. Cell wall D. Cell membrane E. Chloroplasts F. Ribosome G. Chromosomes H. Nucleus I. Nuclear membrane J. Nucleolus K. Mitochondria L. Cytoplasm M. Golgi bodies VI. TRANSPORT 1. PASSIVE TRANSPORT: High low, WITH CONC GRADIENT, NO ENERGY REQUIRED b. What happens to a cell if it’s placed in salt water? • Water leaves the cell (osmosis) cell shrivels up b. What happens if it is placed in pure water? • Water enters the cell (osmosis) swells 2. ACTIVE TRANSPORT – • low to high, • AGAINST CONCENTRATION GRADIENT • ENERGY REQUIRED a. Label each diagram as diffusion, osmosis, or active transport. 1. Active transport 2. Diffusion (passive transport) 3. Osmosis H2O H2O H2O H2O H2O H2O VII. RESPIRATION – glucose broken down to produce ENERGY (ATP), MITOCHONDRIA TYPES: 1. AEROBIC RESPIRATION – uses oxygen, 36 ATP 2. a. Label the equation below. C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O + 36ATP glucose oxygen carbon water dioxide energy 2. ANAEROBIC RESPIRATION – fermentation, does not require oxygen, produces only 2 ATP a. ALCOHOLIC FERMENTATION (yeast) C6H12O6 alcohol + CO2 + 2ATP b. LACTIC ACID FERMENTATION (muscles) C6H12O6 lactic acid + CO2 + 2ATP VIII. LIVING THINGS a. UNICELLULAR ORGANISM – • A living thing made up of only once cell b. MULTICELLUAR ORGANISM – • A living thing made up of 2 or more cells c. 5 LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION IN A MULTICELLULAR ORGANISM CELLS TISSUES ORGANS ORGAN SYSTEM ORGANISM d. HOMEOSTASIS – • Maintaining a stable, internal environment PART 6. CLASSIFICATION I. CLASSIFICATION – grouping organisms according to similar characteristics 1. PROKARYOTIC CELL – • Cell that does not contain a nucleus • (Bacteria) 2. EUKARYOTIC CELL – • Cell that has a nucleus • Make up multicellular organisms II. 7 LEVELS OF CLASSIFICATION: KINGDOM PHYLUM CLASS (largest, most diverse) ORDER FAMILY GENUS SPECIES (smallest, most similar) Kings Play Chess On Fine Green Stools III. BINOMIAL NOMENTCALTURE • Genus species 3. Example: Homo sapiens Homo = Genus, sapiens = species IV. 6 KINGDOMS 1. Fill in the missing parts of the chart. KINGDOM CHARACTERISTICS EXAMPLES 1. Eubacteria -unicellular 2. unicellular -prokaryotic -heterotrophic or autotrophic Bacteria found in extreme environments (thermal vents) -unicellular Animal like = ameba, paramecium Plant like = algae, euglena Archaebacteria 3. PROTISTS -prokaryotic -heterotrophic or autotrophic -eukaryotic -heterotrophic or autotrophic Bacteria found everywhere KINGDOM CHARACTERISTICS EXAMPLES 4. FUNGI -heterotrophic -mostly multicellular Mushroom, yeast, mold, mildew 5. PLANT -multicellular -autotrophic Trees, grass, flowers… 6. ANIMAL -multicellular -heterotrophic Jellyfish, humans, cats, dogs, fish, grasshoppers, bears… HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS PART 7. SKELTAL SYSTEM I. FUNCTIONS 1. movement 2. protection & support 3. makes blood cells 4. shape 5. stores materials (calcium & phosphorus) II. PARTS 1. BONES – 206 in body • bone marrow – produces blood cells 2. CARTILAGE a. flexible b. protection & support c. cushioning (bw vertebrae) d. make up body parts (nose, ears) e. end of bones 3. TENDONS – connective tissue which connects MUSCLES TO BONES 4. LIGAMENTS – connective tissue which connects BONE TO BONE 5. JOINT – where 2 bones meet • a. immoveable – skull • b. pivot – neck (side to side, up & down) • c. ball and socket – hip, shoulder (circular) • d. hinge – elbow, knee (back & forth) • e. gliding – wrist (all directions) PART 8. MUSCULAR SYSTEM I. FUNCTION • LOCOMOTION (movement) by contracting and relaxing of the muscles II. TYPES OF MUSCLES Fill in the missing parts of the chart below. MUSCLE VOLUNTARY/INVOL 1. voluntary SKELETAL MUSCLE 2. Smooth Muscle INVOLUNTARY 3. CARDIAC MUSCLE Involuntary STRIATED/NON LOCATION STRIATED attached to bones NONSTRIATED digestive striated system, blood vessels.. HEART 4. How do skeletal muscles WORK IN PAIRS> • One contracts while the other relaxes. 5. Which muscle is contracting? • Bicep Relaxing? • Tricep PART 9. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM I. FUNCTION – NUTRITION a. INGESTION – taking in of food b. DIGESTION – the breakdown of food c. EGESTION – the removal of undigested wastes II. NUTRIENTS – substances needed by the human body 1. CARBOHYDRATES • sugars & starches • provide ENERGY 2. PROTEINS • amino acids • build & repair 3. LIPIDS • Energy, protection, insulation 4. VITAMINS - normal functioning 5. MINERALS - normal functioning 6. WATER - makes up body, transport, chemical reactions III. 2 TYPES OF DIGESTION 1. MECHANICAL DIGESTION • physical breakdown 2. CHEMICAL DIGESTION • breaking down using ENZYMES IV. PARTS OF DIGESTIVE SYSTEM b. HELPER ORGANS 1. MOUTH -LIVER – makes bile, a. mechanical digestion begins (teeth) EMULSIFICATION of fat b. chemical digestion begins – -GALL BLADDER – stores bile enzymes in saliva, (starches -PANCREAS – pancreatic juice sugar) many enzymes 2. EPIGLOTTIS – closes over trachea to prevent choking c. ABSORBS NUTRIENTS 3. ESOPHAGUS – pushes food to -VILLI – folds that absorb stomach (PERISTALSIS) nutrients into bloodstream. 4. STOMACH 6. LARGE INTESTINE – water a. mechanical digestion - churning absorbed from feces, bacteria food which make vitamins b. chemical digestion of proteins c. mix of food = chyme 7. RECTUM – stores waste 5. SMALL INTESTINE – most (feces) digestion 8. ANUS – where wastes leave occurs, digestion ends the body a. INTESTINAL JUICES many enzymes V. LABEL THE DIAGRAM BELOW. A. Mouth B. Esophagus L A C. Liver D. Gall Bladder B E. Small Intestine C K F. Rectum G. Appendix J D H. Large intestine I. Small intestine I J. Pancreas E H K. stomach G L. Salivary glands F PART 10. CIRCULATORY SYSTEM I. FUNCTION – TRANSPORT II. PARTS 1. HEART – pumps blood a. ATRIA – upper chambers b. VENTRICLES – lower chambers c. VALVES – prevent backflow of blood d. SEPTUM – separates left & right sides 2. BLOOD VESSELS a. ARTERIES – thickest, carry blood AWAY from the heart -AORTA – largest artery -PULSE -GREATEST BLOOD PRESSURE b. VEINS – carry blood to the heart -VALVES -VENA CAVA – largest c. CAPILLARIES – thinnest, oxygen & carbon dioxide are exchanged between blood & cells, connect arteries & veins 3. BLOOD - connective tissue a. PLASMA – liquid, carries materials b. RED BLOOD CELLS – contain hemoglobin, carry oxygen c. WHITE BLOOD CELLS – fight disease d. PLATELETS – blood clotting 4. Label the right and left sides of the heart, label which sides pumps oxygenated & deoxygenated blood, and label all parts of the heart. LEFT OXYGENATED RIGHT DEOXYGENATED A I B H C D G E F A. Aorta B. Left Atrium C. Valves D. Left Ventricle E. Septum F. Lower vena cava G. Right ventricle H. Right atrium I. Upper vena cava A. Red Blood Cell B. Platelet C. White blood Cell D. Plasma III. BLOOD TYPES – depend on antigens found on RBC’s 1. A = A antigens, anti–B antibodies 2. B = B antigens, anti–A antibodies 3. AB = A & B antigens, no antibodies (universal acceptor) 4. O = no antigens, anti–A, anti-B antibodies (universal donor) a. Rh factor – extra proteins on RBC’s Rh + (have proteins), Rh – (don’t have proteins) PART 11. IMMUNE SYSTEM I. FUNCTION – defends the body against disease Pathogen – disease causing organism II. PARTS • 1st Line of Defense: physical barriers (skin, saliva, tears, gastric juice…) • 2nd Line: Inflammatory Response • 3rd Line: Antibodies – produced by WBC’s -attach to pathogens, slow them down III. TYPES: 1. ACTIVE IMMUNITY – immune system produces own antibodies, permanent • a. by acquiring the disease (chicken pox) • b. by receiving a vaccination (weak or dead antigens injected into the body) 2. PASSIVE IMMUNITY – receive antibodies from another organism, temporary • IV. Diseases • a. Infectious Disease = • Caused by pathogen, can be spread • b. Noninfectious Disease = • Not caused by pathogen, cannot be spread a. ALLERGIES – reaction that occurs when the body is sensitive to certain substances 1. Allergen – substance body is sensitive to 2. Body produces HISTAMINES (cause symptoms) b. AIDS • Caused by HIV virus • Kills T- cells destroys immune system PART 12. RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. FUNCTION – Gas Exchange II. PARTS 1. NASAL CAVITY • a. mucus – moistens air, traps materials • b. cilia – filters air • c. blood vessels – warm air 2. PHARYNX - throat 3. LARYNX – vocal cords (voice box) 5. TRACHEA – windpipe made of rings of cartilage 6. BRONCHI – 2 tubes that branch off trachea 7. ALVEOLI – air sacs surrounded by capillaries where oxygen & carbon dioxide are exchanged by diffusion 8. DIAPHRAGM – sheet of muscle under lungs III. LABEL THE DIAGRAM BELOW A B F C G D H I E J A. Nasal cavity B. Mouth C. Larynx D. Bronchi E. Diaphragm F. Pharynx G. Trachea H. Bronchi I. Bronchial tube J. Alveoli IV. BREATHING 1. INHALATION (breathing in) a. diaphragm contracts (down) b. air pressure decreases 2. EXHALATION (breathing out) a. diaphragm relaxes (up) b. air pressure increases 3. Breathing rate increases when amount of carbon dioxide in the blood increases. 4. Label the BELL JAR below A. Trachea A B C D B. Bronchi C. Alveoli D. Diaphragm PART 13. EXCRETORY SYSTEM I. FUNCTION – EXCRETION – removal of cellular 4. URINARY SYSTEM (metabolic wastes) • a. KIDNEYS – nephrons II. PARTS that filter the blood & 1. LIVER: Produces maintain water balance UREA, produces URINE (water, DETOXIFICATION urea, salt) 2. LUNGS – excrete CO2 • b. URETERS – carry urine & H20 from kidneys to the bladder 3. SKIN • c. URINARY BLADDER – • a. excretes stores urine perspiration (water, • d. URETHRA – carries urea, salt) urine out of the body • b. maintains body temperature III. Label the parts of the urinary system. A A. Kidney B. Ureter B C. Urinary bladder C D D. Urethra PART 14. NERVOUS SYSTEM I. FUNCTION 1. REGULATION a. processes & sends out messages b. control & coordination c. helps to maintain homeostasis II. PARTS 1. What is a NEURON? • NERVE CELL 2. IMPULSE – message sent by neurons a. STIMULUS – change in the environment that starts an impulse 3. RECEPTOR – sense organs, pick up stimuli (ears, eyes, nose, skin, tongue) 4. EFFECTOR – parts of the body that responds to a stimulus (MUSCLES & GLANDS) 5. PARTS OF A NEURON a. dendrites – branches at start of neuron that pick up impulses b. cell body (cyton) – contains nucleus c. axon – long single fiber that carries impulse to end of neuron (surrounded by myelin) d. terminal branches – branches at end of neuron 6. What is a SYNAPSE? • SPACE BETWEEN EACH NEURON 7. NEUROTRANSMITTER – substances released into a synapse that “carries” impulse to next cell 8. Label parts of the neuron below. F A. Dendrites D. Terminal Branches B. Cell body / Cyton E. Synapse C. Axon F. Schwann Cells III. TYPES OF NEURONS • • • SENSORY NEURON – receptors brain & spinal cord INTERNEURONS – make up brain & spinal cord MOTOR NEURONS – brain & spinal cord effectors IV. RELEX ARC (RSIME) Receptor Sensory Neuron Interneuron Motor Neuron Effector (Interneurons) V. REFLEX 1. Reflex – involuntary response controlled by the spinal cord VI. DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM 1. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM – brain & spinal cord 2. PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM – branching nerves that carry messages to all body parts VII. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM 1. BRAIN (3 parts) – protected by cranium a. Cerebrum – largest • controls VOLUNTARY activities. the senses, thinking, memory, language… b. Cerebellum – back • controls BALANCE c. Medulla – brain stem • controls all INVOLUNTARY activities (heart beat, breathing, digestion…) d. Label the parts of the central nervous system below. A. Cerebrum B. Cerebellum C. Medulla D. Spinal Cord 2. SPINAL CORD – protected by vertebrae PART 15. ENDOCRINE SYSTEM I. FUNCTION 1. REGULATION - produces hormones that control body functions 2. HORMONE a. chemical produced by endocrine glands b. chemical messengers that travel through the BLOODSTREAM a. How are the nervous & endocrine systems similar? • Both send messages. • Both regulate the body/ maintain homeostasis b. How are they different? • The endocrine system uses hormones that travel in the blood to send messages while the nervous system uses impulses that pass over neurons. • Nervous system is faster than the endocrine system. II. PARTS 1. HYPOTHALAMUS – part of brain that, controls the pituitary gland 2. PITUITARY GLAND - in the brain • secretes hormones that control other glands • secretes Growth hormone 3. THYROID – controls metabolism 4. PARATHYROIDS – controls calcium levels 6. ADRENAL GLANDS – on top of each kidney • ADRENALINE – released in times of stress (increases heart rate, breathing rate…) 7. ISLETS OF LANGERHANSon pancreas • INSULIN – decreases blood sugar level • GLUCAGON – increases blood sugar level 8. OVARIES – female gonads • ESTROGEN – secondary sec characteristics 9. TESTES – male gonads • TESTOSTERONE - secondary sex characteristics III. NEGATIVE FEEDBACK 1. How endocrine glands work 2. A hormone causes a gland to produce or stop producing another hormone IV. LABEL THE DIAGRAM BELOW A. Pituitary Gland B. Thyroid C. Parathyroid D. Thymus E. Adrenal Glands F. Islets of Langerhans G. Ovaries H. Testes PART 16. REPRODUCTION & DEVELOPMENT I. ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION 1. 1 parent 2. offspring identical to parent 3. MITOSIS = 1 cell 2 cells II. MITOSIS – cell division 1. 1 cell 2 cells that have the SAME # OF CHROMOSOMES as parent cell 2. asexual reproduction 3. production of ALL body cells EXCEPT sex cells 4. Growth and repair III. STEPS OF MITOSIS: 1. INTERPHASE – chromosomes replicate 2. PROPHASE – nuclear membrane disappears and spindle fibers form 3. METAPHASE – chromosomes line up in middle of cell 4. ANAPHASE – chromosomes separate and move away from each other 5. TELOPHASE – nuclear membrane starts to reform • cytokinesis – cell membrane pinches in IV. Label the steps of mitosis below. A. Interphase D. Anaphase B. Prophase E. Telophase C. Metaphase PLANT CELL MITOSIS 1. no centrioles 2. CYTOKINESIS – cell plate forms instead of cell membrane pinching in IV. TYPES OF ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION 1. FISSION – equal division (bacteria, ameba and paramecium) 2. BUDDING – unequal division (Yeast) 3. SPORULATION – spores develop into new organism (mold, mushrooms) 4. VEGETATIVE PROPAGATION – used by plants (NO SEEDS) -runners (strawberries), buds/tubers (potatoes), grafting (roses), bulbs (onions) V. SEXUAL REPRODUCTION 1. 2 parents, each give sex cell 2. Offspring NOT identical to parents 3. FERTILIZATION = SPERM + EGG ZYGOTE 4. ZYGOTE DEVELOPS INTO EMBRYO (1st 8 weeks) FETUS VI. MEIOSIS – cell division 1. 2 divisions (1 2 4) 2. for sexual reproduction 3. 4 new daughter cells with ½ the number of chromosomes as parent cell 4. TO PRODUCE SEX CELLS ONLY (in ovaries & testes) MALES = 4 SPERM CELLS FEMALE = 1 EGG + 3 POLAR BODIES 5. What type of organisms carry out external fertilization? • Aquatic (fish, frogs…) 6. Why do these organisms release many sex cells at one time? • To increase chance of fertilization 7. What type of organisms carry out internal fertilization? • Terrestrial (live on land) • VII. Metamorphosis • a. Complete = 4 stages (egg larva pupa adult), butterfly • b. Incomplete = 3 stages = egg nymph, adult PART 17. REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM I. FUNCTION 1. REPRODUCTION -the process through which living things produce new individuals of the same kind II. MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM SPERM CELLS – male sex cells 1. TESTES -produce sperm cells and testosterone 2. SCROTUM -external organ that surrounds testes 3. SPERM DUCTS/VAS DEFERENS -tubes that carry sperm to the penis 4. GLANDS -adds liquid to sperm (semen) 5. PENIS –deposits sperm into female 6. URETHRA – tube in the penis which transports urine & semen 7. Label the diagram of the male reproductive system. A A. Urinary bladder B B. Vas Deferens C C. Glands D. Gland D H E. Testes E F. Urethra G. Penis F G H. Vas Deferens III. FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM EGGS – female sex cells 1. OVARIES - makes eggs and estrogen 2. FALLOPIAN TUBES - (oviduct) tubes in which an egg travels through from ovaries to the uterus • FERTILIZATION OCCURS HERE 3. UTERUS - muscular organ where zygote attaches and develops into a baby 4. CERVIX - lower end of the uterus 5. VAGINA – birth canal, where sperm is deposited 6. Label the diagram of the female reproductive system. A. Oviduct / Fallopian Tube A B. Egg (Ovulation) C. Ovary D. Uterus E. Vagina F. Cervix B C F D E IV. MENSTRUAL CYCLE (28 days) 1. STEPS • a. Egg develops in ovary • b. OVULATION – egg released from ovary • c. Lining of uterus thickens with blood • d. NO FERTILIZATION MENSTRUATION (uterus lining sheds, egg leaves body) V. EMBRYONIC DEVELOPMENT 1. FERTILIZATION: EGG + SPERM ZYGOTE (fertilized egg) 2. ZYGOTE EMBRYO (8 weeks) FETUS (after 8 weeks) (BY CELL DIVISION) 3. Label the diagrams. C A B A. Fertilization B. Zygote C. mitosis E F 4. STRUCTURES FORMED a. AMNIOTIC SAC – surrounds fetus & contains amniotic fluid that protects baby b. PLACENTA – network of blood vessels where nutrients & wastes are exchanged between the mother’s blood & baby’s blood by diffusion c. UMBILICAL CORD – blood vessels that connect the fetus to the placenta • Carry nutrients & and wastes to and from the placenta d. Label the diagram below. F B E A. Amniotic Sac B. Uterus C. Cervix D. Umbilical Cord E. Placenta F. fetus C VI. SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN PLANTS (FLOWERS) 1. PARTS OF A FLOWER a. PETALS – colored leaves, attract insects for pollination b. SEPALS – green leaves, protection c. STAMEN – male reproductive organ • ANTHER – produces pollen (sperm) • FILAMENT – stem holds up anther d. PISTIL – female reproductive organ • STIGMA – sticky part that catches pollen • STYLE – long tube that brings pollen to ovary • OVARY – where eggs are produced and stored • OVULES – in ovary, contain eggs 2. Label the diagram of the flower below. 1. anther 10 2. filament 4. stigma 5. style 11 6. ovary 8. petal 9. sepal 10. stamen 11. pistil VIII. HOW DO FLOWERS REPRODUCE? 1. POLLINATION - pollen lands on stigma a. self-pollination – pollen from one flower lands on stigma of the same flower (IDENTICAL) b. cross pollination – pollen from one flower lands on stigma of other flower 2. FERTILIZATION 1. pollen lands on stigma 2. pollen tube grows down through the style and carries pollen to ovary 3. sperm fertilizes egg in ovule 4. ovule SEED (embryo) 5. ovary FRUIT 3. SEEDS • Embryo • Seed coat (protects embryo) • Stored food for embryo 4. GERMINATION – growth of plant embryo inside seed (sprouting) a. For germination to occur there must be enough water, enough oxygen & right temperature PART 18. GENETICS I. GREGOR MENDEL – crossed pea plants to study heredity passing on of traits) I. CHROMOSOMES –in nucleus • 1. consist of genes which contain genetic information (DNA) • 2. sex chromosomes – determine sex of an organism a. EGGS = X SPERM = X or Y b. FEMALE = XX MALE = XY 1. GENES – 2 genes (ALLELES) for every trait (1 from each parent) 2. DOMINANT GENE/TRAIT – stronger gene – CAPITAL LETTER (T) 3. RECESSIVE GENE/TRAIT – weaker gene – lower case (t) 4. PHENOTYPE – physical appearance (what offspring look like) 5. GENOTYPE – genetic makeup T = tall plant, t = short plant GENES PHENOTYPE TT tt Tt GENOTYPE Tall Homozygous OR pure dominant Short Homozygous OR pure recessive Tall Heterozygous OR hybrid III. PUNNETT SQUARES 1. Cross a pure dominant tall plant with a hybrid plant. T t T T TT TT Tt Tt Phenotype = 100% tall Genotype = 50% pure dominant 50% hybrid 2. B = Brown eyes, b = blue eyes Cross a blue eyed person with a hybrid brown eyed person. Give the phenotypes & genotypes of their offspring. b b B Bb Bb b bb bb Phenotype = 50% brown eyes 50% blue eyes Genotype = 50% pure recessive 50% hybrid 3. G = green, g = yellow Cross a yellow plant with a pure dominant plant. Give the phenotypes & genotypes for all offspring. G g g Gg Gg Phenotype = 100% green Gg Genotype = 100% hybrid G Gg IV. MULTIPLE ALLELES – MORE THAN 2 GENES AVAILABLE FOR A TRAIT 1. Example: BLOOD TYPES – 3 alleles a. A & B = both dominant b. O = recessive BLOOD TYPE A B AB O ALLELES AA or AO BB or BO AB OO 2. Cross a person with blood type O with a person who is pure for blood type B. What blood types will their children have? O O B BO BO B BO BO All of their children will have blood type B. V. MUTATION – change in a gene that may cause a new trait (good or bad) • a. in SEX CELLS can be passed on to offspring • b. Examples: sickle cell anemia VI. PEDIGREE CHARTS - trace a genetic trait in a family 1. Example: 2. The pedigree chart below traces the appearance of earlobes through 3 generations of a family. Based on the chart, attached earlobes is a a. dominant trait b. recessive trait c. mutated trait d. trait common in females VII. APPLIED GENETICS 1. Selective Breeding: crossing organisms with desirable traits to produce offspring with those traits A. Hybridization (different) B. Inbreeding (same/similar) 2. Genetic Engineering: • Recombinant DNA made simple organism carried out function controlled by complex organisms cut DNA • (Example: Insulin producing bacteria) 3. Cloning: producing organism (CLONE) that is genetically identical to parent PART 19. PLANTS I. PARTS OF PLANTS 1.ROOTS: absorb water & dissolved minerals, anchor plant, store food b. root hairs – increase surface area for water absorption 2. STEM a. supports plant, hold up leaves b. contains VASCULAR TISSUE -XYLEM – carries water up the plant -PHLOEM – carries food everywhere 3. LEAVES – where PHOTOSYNTHESIS occurs a. chloroplasts – contain chlorophyll (green pigment which absorbs light) b. Equation: 6CO2 + 6H2O C6H12O6 + 6O2 (carbon (water) (glucose) (oxygen) dioxide) c. SUNLIGHT = energy source d. OXYGEN = waste product that is released into the air (oxygen we breathe) TROPISM – how a plant responds to a stimulus • POSITIVE = toward stimulus (Example: light) NEGATIVE = away from stimulus PART 20. ECOLOGY I. ECOSYSTEMS 1. ECOSYSTEM: • all the living & nonliving things in an environment a. BIOTIC FACTORS – living things b. ABIOTIC FACTORS – nonliving things 2. COMMUNITY – all of the different LIVING things in an ecosystem 3. POPULATION – organisms of the same SPECIES living in a community 4. NICHE a. the role an organism plays b. what it needs, what it eats, where it lives, how it behaves 5. HABITAT – where an organism lives II. LIVING THINGS IN AN ECOSYSTEM 1. PRODUCERS • autotrophs (plants), • get energy from the SUN • GREATEST AMOUNT OF ENERGY IN THE ECOSYSTEM 2. CONSUMERS – heterotrophs a. HERBIVORES – eat producers (plants) b. CARNIVORES – eat other animals c. OMNIVORES – eat both plants and animals d. SCAVENGERS – eat dead organisms 3. DECOMPOSERS a. break down dead organisms into small materials & place them back into the environment to be used again b. BACTERIA, MUSHROOMS 4. PREDATOR – living thing that hunts and kills other living things as food 5. PREY – organisms killed by predators III. FOOD CHAIN - shows how much ENERGY is transferred 1. PRODUCER PRIMARY CONSUMER SECONDARY CONS (herbivore or omnivore) (carnivore or omnivore) 2. Label the parts of the food chain below. b. d. e. c. Primary Secondary Tertiary producer carnivore consumer consumer consumer (herbivore) a. 3. Where is the most energy found in this food chain? Plants IV. FOOD WEB – overlapping food chains 1. Identify the following organisms in the food web. a. Producers: Grasses, bean plants b. Herbivores: Rabbits, caterpillars c. Carnivores: Frogs, trout, snakes, hawks, foxes d. decomposers: bacteria V. ENERGY PYRAMID Use the energy pyramid at the right to answer the questions below. a. Which level contains the greatest amount of energy? • GREEN PLANTS b. What happens to the amount of energy as it moves up the pyramid? • IT DECREASES c. Which organism is an herbivore? • MICE VI. SYMBIOSIS 1. Relationship between 2 organisms where one lives on, in, or near the other 2. 3 types: a. COMMENSALISM = 1 benefits, other not harmed/unaffected (+, -) -mites on eyebrows b. MUTUALISM = both benefit (+, +) -bacteria in our intestines c. PARASITISM = PARASITE benefits, HOST is harmed (+, -) -fleas on dogs VII. ECOLOGICAL SUCCESSION 1. When one community replaces another until a stable community exists 2. CLIMAX COMMUNITY – stable community, end of succession Pioneer organisms Climax community VIII. CYCLES 1. Water Cycle (evaporation, condensation, precipitation, transpiration) 2. Carbon & Oxygen Cycle (respiration & photosynthesis 3. Nitrogen Cycle (Nitrogen changed into usable forms) PART 21. EVOLUTION I. EVOLUTION – change in a species over time II. EVIDENCE OF EVOLUTION 1.FOSSILS – remains of living things 2.a. Law of Superposition – younger layers of sedimentary rock lay on top of older ones b. In the diagram below, which fossil: • • • • OLDEST = A YOUNGEST = C MOST COMPLEX = C MOST SIMPLE = A 2. ANATOMICAL EVIDENCE a. Homologous structures – structures that evolved from similar body parts (similar structure BUT different function) b. Examples: human arm, whale flipper, dog leg, bat wing 3. EMBRYOLOGICAL EVIDENCE a. young embryos of different organisms are similar 4. CHEMICAL EVIDENCE a. materials that make up organisms are similar (proteins, DNA) ***ALL OF THIS EVIDENCE SUPPORTS THE THEORY OF EVOLUTION AND SUGGESTS THAT PERHAPS ALL ORGANISMS EVOLVED FROM COMMON ANCESTORS.*** III. CHARLES DARWIN 1. CHARLES DARWIN a. Galapagos Islands b. NATURAL SELECTION 2. NATURAL SELECTION – • those organisms best adapted to their environment will survive & reproduce 3. ADAPTATION – a change that helps an organism better adapt to an environment survive 4. BASED ON 5 MAIN POINTS a. OVERPRODUCTION – organisms produce too many offspring competition natural selection\ b. COMPETETION – limited resources organisms compete natural selection c. VARIATION – differences between organisms best adapted will survive & reproduce Example: Polar bears with thicker fur will survive & reproduce d. SURVIVAL OF THE FITTEST – those best adapted will survive & reproduce e. SPECIATION – over time favorable adaptations survive & unfavorable disappear new species IV. GRADUALISM: • evolution happens slowly over time V. PUNCTUATED EQUILIBRIUM: • long periods of time with no change interrupted by short periods of change EXTRA REVIEW QUESTIONS 1. Identify the steps of scientific method. 2. Describe the 2 types of variables. 3. Why do investigations require a control? 4. Explain the cell theory. 5. Distinguish between eukaryotes and prokaryotes. 6. Describe the function of the cell nucleus. 7. Identify the main functions of the cell membrane and the cell wall. 8. Describe what happens during diffusion. 9. Identify the organization levels in multicellular organisms. 10. Compare and contrast the structure of a plant cell with that of an animal cell. 11. What are the contributions of the early cell scientists? 12. Compare and contrast active and passive transport. 13. Assume that MITOSIS begins with eight chromosomes in the nucleus of a cell. When telophase ends, how many chromosomes will be present in each new nucleus? 14. Contrast the chromosome number of body cells and gametes. 15. Contrast meiosis and mitosis. 16. What happens to the number of chromosomes per cell during meiosis? 17. Explain how sex is determined. 18. Summarize nondisjunction and the problems it causes. 19. A person who has type AB blood is sometimes referred to as a universal recipient. Why? 20. Summarize the relationship between genes and DNA. 21. Describe the overall structure of the DNA molecule. 22. Summarize the events of DNA replication. 23. Before undergoing meiosis, a cell has 28 chromosomes .How many are present in each of the four daughter cellsafter meiosis? 24. What kinds of cells are produced in the process of meiosis? 25. Small ears in guinea pigs are dominant over large ears. A homozygous dominant male (EE) is crossed with a heterozygous (Ee) female. What is the chance that large-eared offspring will be produced? 26. Which Kingdom includes only prokaryotic organisms? 27. In what cell structure does aerobic cellular respiration take place? 28. When oxygen is present, cellular respiration in your body cells produces a total of ______ ATP. 29. Respiration without oxygen is called ___ respiration. 30. In what cell structure does photosynthesis take place? 31. Which type of cells in a plant normally have the most chloroplasts? 32. How is genetic information from parents transferred to their offspring? 33. If one strand of DNA is AAATTTCCCGGG, what is the complementary strand? 34. What is a mutation? 35. When mutations occur in sex cells, are they passed on to offspring? What about mutations that occur in somatic cells? 36. T=tall, t=short. Cross a parent that is homozygous dominant with another parent that is heterozygous. Give the genotype and phenotype of the offspring. 37. What is the difference between dominant and recessive genes. 38. What part of the cell is the site of protein synthesis? 39. What part of the cell contains the genetic material of the cell? 40. What part of the cell is site of cellular respiration? 41. What part of the cell packages and sorts materials? 42. What part of the cell stores materials? 43. What part of the cell contains digestive enzymes for digestion? 44. A and B alleles are dominant, and O is recessive. John, who has blood type O, marries Sue, who has blood type AB. What blood types will their offspring potentially have? 45. What is the primary function of photosynthesis? 46. If black is dominant (B) and white is recessive (b), what are the phenotypes and genotypes of a cross between two heterozygous parents? 47. Why is a person with AIDS unable to combat infections? 48. a. 11.2cm = ___ mm b. 2.7 mm = _____ km c. 9.2 cm = ___ mm 49. Water freezes at _____ degrees centigrade (Celsius). 50. Water boils at _____ degrees centigrade (Celsius). 51. What is meant by the word phenotype? 52. Describe the process of cytokinesis in plant cells. 53. Identify and explain the three types of symbiosis. 54. What is an ecosystem? 55. What is the difference between a community and a population? 56. Which land biome contains the greatest variety of living things? 57. Which land biome consists of trees that lose their leaves during the fall? 58. Which land biome consists of coniferous trees? 59. The tundra is made up of permafrost? What is permafrost? 60. What is evolution? 61. What is natural selection? 63. Explain the Law of Superposition.