* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download No Slide Title
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Molecular Inversion Probe wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
SNP genotyping wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and archaeogenetics of South Asia wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genome-wide association study wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Human leukocyte antigen wikipedia , lookup
Microsatellite wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
A30-Cw5-B18-DR3-DQ2 (HLA Haplotype) wikipedia , lookup
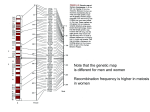
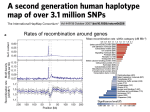
Genes in human populations Population genetics: focus on allele frequencies (the “gene pool” = all the gametes in a big pot!) Hardy-Weinberg calculations (e.g., p2 + 2pq + q2) assume: – Mating is random (but there is stratification and assortative mating) – Population is large (if appropriately chosen!) – No mutation (but there is) – No migration (but migration occurs) – No selection (but there can be selection) DNA typing and forensics Common genetic polymorphisms – RFLPs – VNTRs – Microsatellites For each variable locus, the frequency of alleles in a population can be determined - suspect typed for many loci and probability of match determined (exclusion criteria) Conservation of genomic segments (haplotypes): The “HapMap” In populations, it appears the the linear order of alleles (“haplotype”) is conserved in uninterrupted blocks or “neighborhoods” that tend to be inherited together, with recombination occurring between them Most population share common SNP variants and haplotypes Haplotype blocks and the tag SNPs that identify them will form the HapMap