* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrial DNA wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Sex-limited genes wikipedia , lookup
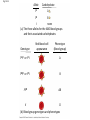
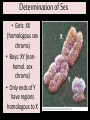
Mendel Law Exceptions and Sex Linkage Big Idea 3: Living systems store, retrieve, transmit, and respond to info essential to life processes. Essential Knowledge • 3A4: The inheritance pattern of many traits cannot be explained by simple Mendelian genetics. Incomplete Dominance • Cross white roses (WW) with red roses (RR) Pink roses (RW)! • Heterozygous offspring are in b/t the 2 homozygous phenotypes. BLENDING! Codominance • A condition in which both alleles show up in phenotype. • Neither allele is recessive. Codominance Codominance: Piebald BlackPastel Ball Python Polygenic Traits • Traits that are controlled by 2 or more genes. • Ex: skin/eye color in humans controlled by > 4 genes Creates wide range of trait Multiple Alleles • Some genes have more than 2 alleles. • Ex: Blood type: 4 phenotypes: A, B, AB, O • Alleles: i, iA, or iB • But, still only get 2 copies of allele, from mom and dad! Fig. 14-11 Allele IA Carbohydrate A IB B none i (a) The three alleles for the ABO blood groups and their associated carbohydrates Genotype Red blood cell appearance Phenotype (blood group) IAIA or IA i A IBIB or IB i B IAIB AB ii O (b) Blood group genotypes and phenotypes Gene Linkage • Genes for traits can be inherited together linked. • Each chromosome is actually a group of linked genes. Can you tell which traits are linked? Determination of Sex • Girls: XX (homologous sex chroms) • Boys: XY (nonhomol. sex chroms) • Only ends of Y have regions homologous to X X Y Sex Linked Genes • Found on sex chroms, mainly X (contains more DNA). • Easy to spot b/c many males will have trait XY..if trait is on X, no competition on Y (less DNA) Fruit Fly Genetics! • Good for genetic studies (Drosophila melanogaster: breed at a high rate A generation can be bred every 2 weeks Only have 4 pairs of chromosomes • Wild type = normal phenotype • Traits alternative to wild type: mutant phenotypes Some Traits are Sex Limited and Expression Depends on Sex of Individual Some Traits Result from Nonnuclear Inheritance • Ex: Chloroplasts and mitochondria are randomly assorted to gametes and daughter cells In Animals… • Mitochondrial DNA is passed on by egg, not sperm inherit mitochondria traits from mom. Let’s do a Problem! Sex Linked Fruit Fly Sample Probs and Lab