* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Punnetts 2
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in learning and memory wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Copy-number variation wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
The Selfish Gene wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
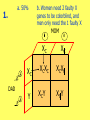
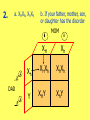
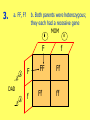
Punnetts 2 - Answers a. 50% 1. b. Women need 2 faulty X genes to be colorblind, and men only need the 1 faulty X MOM XC XC DAD Y XCXC XCY XC XCXC XCY 2. a. XHXh, XhXh b. If your father, mother, son, or daughter has the disorder MOM XH Xh DAD Y XHXh XHY Xh XhXh XhY 3. a. FF, Ff b. Both parents were heterozygous; they each had a recessive gene MOM F F DAD f FF Ff f Ff ff #2 on Pg. 203 • Because males have only one X chromosome, they show all the traitsgenes on that X. Females have two X’s, so they have two chances to get a gene that is good, and can show the good trait. Example: If females, have one gene on an X for colorblindness, and one gene on the other X for normal vision, she will have normal vision. • incomplete dominance – when neither gene is dominant, you have a blend (Ex: red gene + white gene = pink flower) • codominance – when both genes show up as a trait (Ex: red gene + white gene = red and white spots) (Ex: type A gene + type B gene = type AB blood) • polygenic – when more than 1 pair of genes controls a trait (Ex: skin color, eye color, hair color)