* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 21-Thalassemia
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Essential gene wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
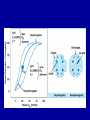
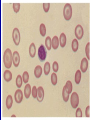
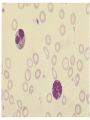
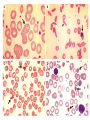
Hemoglobinopathies Diseases affecting the structure, function or production of Hb. Types 1- Structural Hemoglobinopathies A- Abnormal Hb polymerization --- Sickle cell anemia B- Altered O2 affinity --- High affinity – polycythemia --- Low affinity – Cyanosis, pseudo anemia C- Hb that oxidize readily --- Unstable Hb (HA, jaundice) --- MetHb (cyanosis) 2- Thalassemia (defective biosynthesis of globin chains) A- α-thalassemia B- β-thalassemia C- δβ, γδβ, αβ thalassemias 3- Thalassemic Hb variants (structurally abnormal Hb associated with coinherited thalassemic phenotype) A- Hb-E B- Hb - Constant spring C- Hb- Lepore 4- Hereditary persistence of fetal Hb (HPHF) (Hb F in adults) 5- Acquired Hemoglobinopathies A- Met-Hb due to toxic exposure. B- Sulf-Hb due to toxic exposure. C- CarboxyHb due to CO. D- Hb-H in erythroleukemia. E- Elevated Hb-F in states of erythroid stress & BM dysplasia. Thalassemia This is an inherited disorder of α or β globin chain biosynthesis. Causes reduced production of Hb tetramers causing hypochromia µcytosis. The latter is leading to ineffective erythropoiesis & hemolytic anemia. Normal Hb consists of 2α and 2β chains. Two clusters of genes encode for globin synthesis (β genes on chromosome 11 & α genes on chromosome 16). An unbalanced accumulation of α or β chains results α- Thalassemia Decreased α-chain production relative to βchain production forming β4 (Hb-H inclusion bodies). RBCs bearing inclusion bodies are rapidly removed from the circulation by RES cells thus shortening RBC survival. S&S Deletion of 1 gene (-α/αα) & 2 genes (-/αα; -α/α) are virtually asymptomatic. Deletion of 3 genes (--/-α) producing Hb H disease (Hb Barts). Moderate hypochromic microcytic anemia & splenomegaly. Hb= 8-10 g/dL, special stain shows Hb H inclusions. Hb electrophoresis shows Hb H. Hb H tends to precipitate during oxidative stress & under increased temperature as in infections causing hemolysis. Deletion of 4 genes (--/--) is the most severe form that is incompatible with life leading to intrauterine death of the fetus (hydrops fetalis). β- Thalassemia Decrease in β-chain production relative to αchain production. Common in Mediterranean, Asian & African populations (areas endemic with malaria). Trait --- asymptomatic. Clinical anemia ---- is seen in homozygous or compound heterozygous e.g. β thalassemia/Hb E. Reduced β globin chain synthesis leads to accumulation of free α globin chains that precipitate in early erythroblast development since they are insoluble. These lead to ineffective erythropoiesis in BM & enhanced destruction in circulation. Anemia, splenomegaly ± hypersplenism, osteoporosis, skeletal & soft tissue changes due to BM expansion, iron overload ( ↑GIT absorption & blood transfusion) deposit in liver, heart, pancreas, pituitary & other endocrine organs. Lab. Dx Microcytic hypochromic anemia, MCV ↓. Hb- electrophoresis --- Hb A2 ↑ > 4-6%, Hb F ↑ 5-20%. PCR, DNA probes. Antenatal Dx --- Amniotic fluid analysis & chorionic villous sampling. ℞ α-thalassemia ---- 1 gene or 2 genes deletion may be asymptomatic and require no treatment. Hb H disease- Folic acid 1mg/day orally Splenectomy for progressive anemia. β thalassemia Improved outcome recently due to the use of aggressive blood transfusion support & effective iron chelation therapy. The only curative ttt by BM transplantation. Blood transfusion – non-transfused pt survives only 2 y in homozygous state. -- Aim to maintain Hb at 11-13g/dL -- Pre-transfusion level>10g/dL -- extend life to 2nd decade, minimize bony abnormalities, and improve sexual development. -- Leukocyte-poor RBCs given to minimize allosenstization & not to prejudice future BMT. -- HB vaccine given for pt with –ve Ab test Splenectomy if transfusion requirement > 1.5 normal (>200ml/kg/year) -- preceded by polyvalent pneumococcal vaccine (pediatric pt also given H influenza & N meningitides vaccine) Iron chelation --- if not given pts will die of iron overload. --- Subcutaneous desferrioxamine 1.5-2.5 g/d --- Oral defroperone, deferasirox --- S.C desferral 12-24 h infusion 5-6x/w --S/E visual disturbances, tinnitus, azotemia, proteinuria. Annual ophth & audiol exam needed. --- Periodic estimation of iron burden (S Fe, TIBC & S Ferritin) --- Estimate of liver iron concentration --- Annual cardiac evaluation to detect early dis --- GTT, thyroid function test, cortisol determination --- Hormone replacement therapy Stem cell transplant Allogeneic BMT for homozygous β thalassemia Manipulation of globin chain gene expression with 5-azacytidine, hydroxyurea, erythropoietin, butyrate analogues to stimulate Hb F synthesis by γ globin chain augmentation Experimental ttt --- gene therapy * For β globin alleles * Still investigational