* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ADHD: The Biology Behind the Behavior Presentation
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
State-dependent memory wikipedia , lookup
Parent management training wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Executive dysfunction wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Biology of depression wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Methylphenidate wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Externalizing disorders wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Sluggish cognitive tempo wikipedia , lookup
Controversy surrounding psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder wikipedia , lookup
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder controversies wikipedia , lookup
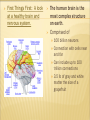
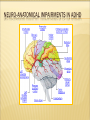
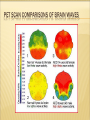
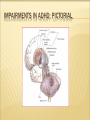
MORABETO MIND LEGACY ASSOCIATES INC. With Instructor: Janice R. Morabeto M.Ed. L.S.W. C.H.T. ON DEMAND TRAINING MODULES Enjoy the fact that you will not have to be traveling today to get your C.E.U. hours met! Get prepared to learn! If you normally take notes during lecture, do that as you take this On demand class. It will help you to remember what you learned better, longer and be able to apply that knowledge when you need it most! Take advantage of downloading and printing the PowerPoint presentations before class begins. Email me at [email protected] if you have questions regarding the content of this material, or if you are interested in future C.E.U. Opportunities. ADHD: A BIO-PSYCHO-SOCIAL APPROACH TO UNDERSTANDING COURSE DESCRIPTION ADHD is the most common psychiatric disorder diagnosed in children in America. It remains, as well, one of the most controversial in terms of diagnosis and treatment approaches. Recently, the fields of neuroanatomy, molecular genetics and neurochemistry are beginning to shed some real light as to the complexities, and actualities of this important disorder. AGENDA: TO EXPLORE THE CURRENT RESEARCH In neuroanatomy as it relates to understanding ADHD as a disorder with specific biological impairments. In molecular genetics to understand how ADHD has been shown to be particularly hereditary In neurochemistry as it relates to understanding ADHD as a disorder with specific neurochemical imbalances. HOW ABOUT A LITTLE REVIEW! Take this 5 question pre-test to review and learn! Spend only 2-3 minutes on it Answers will be reviewed before I continue with the presentation. HOW CAN THIS INFORMATION HELP YOU TO BE MORE EFFECTIVE IN WORKING WITH THESE CHILDREN? Many people feel manipulated by the ADHD individual due to the inconsistencies of their behaviors. Knowing the biology behind the behavior will help you to realize that those who suffer from ADHD have not mastered developmentally appropriate skills; ie, communication, study skills and at times are lagging in maturity True? False? 1. There are three types of ADHD. 2. The three subtypes of ADHD are Inattentive, Hyperactive, and Combined. 3. ADHD is a childhood disorder and evidence of it must first be seen before age 7. 4. Some of the symptoms of ADHD Hyperactive-Impulsive Type are excessive talking, difficulty in moderating impulses, and a state of general over-arousal. 5. Some of the symptoms of ADHD Inattentive Type are forgetfulness, disorganization and a state of general underarousal. PRIMARY SYMPTOMATOLOGY Hyperactive-Impulsive Type Hyperactivity In children Inability to modulate locomotion; squirming , fidgeting, excessive climbing Hyperactivity in Adults Restlessness, irritability, difficulty relaxing HYPERACTIVE-IMPULSIVE TYPE CONT. Impulsivity in children Inability to moderate behaviors i.e. excessive talking, butting into conversations, invading others’ personal boundaries, low frustration tolerance Impulsivity in Adults Continue to be consistent talkers who have not learned to listen to others in a genuine way, tend to change jobs more frequently, have more divorces, traffic violations and substance abuse problems including nicotine, caffeine and overeating INATTENTIVE TYPE In children: Difficulties in memory, listening, following directions, lack of follow through, persistence, transitioning between tasks, daydreaming. In adults Difficulty in memory, planning, organization, follow through in work and in family lives. Less likely to finish high school or college and tend to advance slower than their peers. ON THE OTHER HAND! If they can channel their energy, enthusiasm and love of novelty, they can become very successful in the workplace. Studies show that about 1/3 of adults with ADHD can become entrepreneurs by their 30’s. First Things First: A look at a healthy brain and nervous system. The human brain is the most complex structure on earth. Comprised of 100 billion neurons Connection with cells near and far Can include up to 100 trillion connections 3.5 lb of gray and white matter the size of a grapefruit Dynamic nature – changes constantly in response to environmental stimuli Major Job – to reach and maintain Homeostasis, the regularity of the internal environment, and to integrate and modulate incoming information from our senses Modulates incoming information to ascertain the bodies need for and level of response NEURO-ANATOMICAL IMPAIRMENTS IN ADHD NEURO-ANATOMICAL IMPAIRMENTS IN ADHD Smaller anatomic areas and/or volumes in the following regions of the brain. Some studies suggest as much as 7-10% below the healthy control samples: PET SCAN COMPARISONS OF BRAIN WAVES NEURO-ANATOMICAL IMPAIRMENTS IN ADHD Corpus Callosum Prefrontal Cortex Basal Ganglia Cerebellum NEURO-ANATOMICAL IMPAIRMENTS IN ADHD Locus Coeruleus Reticular Activating System Total White Matter Volume NEURO-ANATOMICAL IMPAIRMENTS IN ADHD Corpus Callosum the large bundle of axons which connect the two cerebral hemispheres. It disseminates information from the cerebral cortex on one side of the brain to the same region on the other side. Prefrontal Cortex Area of the brain that is devoted to many aspects of mature adult functioning such as judgment, reasoning, planning, rational thought, organization goal setting and follow through. NEURO-ANATOMICAL IMPAIRMENTS IN ADHD Basal Ganglia group of structures which coordinate movement; located in the forebrain (telencephalon) Cerebellum structure located in the back of the brain involved in central regulation of movement, such as basic movement, balance, and posture; comes from the latin word meaning "little brain"; is divided into two hemispheres and has a cortex NEURO-ANATOMICAL IMPAIRMENTS IN ADHD Locus Coeruleus Noradrenergic system supplies Norepinephrine (NA) throughout the central nervous system. Involved in processing of relevant or salient information as well as highly involved in startle reactions, stress and panic. Reticular The Activating System RAS acts as the executive secretary conscious awareness. It is the chief gatekeeper that screens or filters the type of information that will be allowed to get through. IMPAIRMENTS IN ADHD: PICTORIAL NEUROTRANSMITTERS RELATED TO IMPORTANT MENTAL PROCESSES AND ADAPTIVE BEHAVIORS WHEN IT COMES TO NEUROCHEMISTRY WELLNESS = BALANCE The three major categories of substances that act as neurotransmitters are Amino Acids Peptides Monamines Amino Acids Glutamic acid or Glutamate GABA Aspartic acid Glycine Workhorses of the Brain Peptides Vasopressin Somatostatin Neurotensin, etc. The peptides perform specialized functions in the hypothalamus or act as co-factors elsewhere in the brain. Monoamines Norepinephrine, Dopamine Serotonin Acetylcholine The monoamines & acetylcholine perform specialized modulating functions and are often confined to specific structures. Dopamine Gusto” Neurotransmitter Implications in motivation, reward and risk taking Predictive of locomotive activity “ Norepinephrine Responsible for sustained attention Fight and Flight Reaction (Little Brain) Prepares the body for action increase the heart rate as well as blood pressure Serotonin Has been called the “Master neurotransmitter” Has Mood, regulatory effects on other neurotrasmitters appetite, concentration, memory, sexual function and arousal ADHD BRAINS LACK NEUROCHEMICAL BALANCE Inattentive Type Norepinephrine Dopamine Serotonin Daydreaming Memory Impairment Difficulty concentrating Hyperactive-Impulsive Type Norepinephrine Dopamine Serontonin Hyperactivity Impulsivity Restlessness WHAT’S HAPPENING IN THE FIELD OF MOLECULAR GENETICS? Are those people related?? FAMILY AND TWIN STUDIES Between 10 and 35 percent of children with ADHD have a firstdegree relative with past or present ADHD. Approximately one-half of parents who had ADHD have a child with the disorder. Over the past decade, a large number of twin studies have shown that, when ADHD is present in one twin, it is significantly more likely also to be present in an identical twin than in a fraternal twin. GENETIC CONTRIBUTIONS TO ADHD Several genes have been consistently found to be a associated with ADHD Dopamine D4 (DRD4) Dopamine Transporter Gene (DAT) Found to be also impaired in Tourettes Conduct Disorder Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder GENETIC CONTRIBUTIONS TO ADHD Dopamine D5 receptor gene (DRD5) Dopamine beta-hydoxylase gene (DBH) Implicated in Decreased concentrations of dopamine Upregulated postsynaptic dopamine (decreased amount available in the synapse) Extracellular concentrations of dopamine Brain’s inability to modulate dopamine levels to control behaviors and mental processes KNOCK OUT MICE New advances in molecular genetics have enabled science to selectively “knock out” one gene in a sample of mice. By observing and contrasting generations of mice with and without a particular genetic influence behaviors can be observed, compared and contrasted. GENETIC CONTRIBUTIONS TO ADHD Serotonin Transporter Gene (5HTTT) Serotonn Receptor Gene (HTR1B) Decreased concentrations of serotonin Upregulated postsynaptic serotonin (decreased amount available in the synapse) Extracellular concentrations of serotonin Brain’s inability to modulate serotonin levels to control behaviors and mental processes IMPORTANT NOTE The genetic contribution to ADHD has been shown to be as high as 75% in some families, but! Other possible causes can be: Other psychiatric disorders in parents and first degree biological relatives Substance use, abuse and dependency in mother, father and alcoholism and substance related disorders in families Other medical problems that could have caused damage to the brain WHEW!!! HOW ABOUT A LITTLE REVIEW! Review Flash Cards under Java Games These will highlight the important aspects of the class and prepare you for the quiz. Complete at least one more game, so that you can enjoy the review of this important information. You will also greatly increase the chances of passing the quiz the first time! You can also review this presentation as many times as you’d like.