* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Prograf® (tacrolimus)
Survey
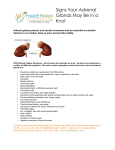
Document related concepts
Discovery and development of proton pump inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Adherence (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
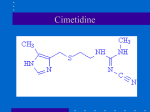
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Psychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
Practical Issues for Dietitians SUPPLEMENTAL SLIDES Presented by David B. Goldwater R.Ph Clinical Consultant Pharmacist March 31, 2011 CONTENTS MEGACE-ES ADVERSE EFFECTS PROGRAF 2 Source: Am J Geriatr Pharmacother 2008; 6:167–172 MEGACE & ADRENAL INSUFFICIENCY 3 MEGACE & ADRENAL INSUFFICIENCY Source: Am J Geriatr Pharmacother 2008; 6:167–172 FOCUS OF CONCERN Malnourished older patients who are given Megestrol acetate could be at risk for adrenal insufficiency. It might be difficult to detect because the signs and symptoms are subtle. CASE STUDY In Kansas City, Missouri, an 80-yearold woman with Dyspnea was being treated for major depression with psychotic features. Her physical functioning had declined. Because she was losing weight, Megestrol acetate was prescribed to stimulate her appetite. 4 DURING HOSPITALIZATION Her Dyspnea worsened. She was transferred to the intensive-care unit, where she was intubated. Her blood pressure dropped. After infectious, cardiac, and neurological causes of hypotension were ruled out, a cosyntropin stimulation test, was performed to exclude adrenal insufficiency. IT INDICATED A SUBOPTIMAL RESPONSE. The medication was discontinued, and steroid replacement was initiated. Blood pressure returned to normal, and the patient slowly improved. She was weaned from the ventilator several weeks later. 5 OUTCOME Two months later, her respiratory function improved, and cosyntropin stimulation test findings were normal. Chronically ill, malnourished elderly patients with adrenal insufficiency may experience depression and reduced appetite, making the diagnosis difficult. In this case, adrenal insufficiency was not suspected at first because the presentation was unusual, The patient’s clinical history was complicated by other illnesses, and she had NOT been using Megestrol for a long time. 6 MEGACE-ES CONCLUSION/ RECOMMENDATION For patients who need more than 12 weeks of treatment with Megestrol…... Free cortisol levels should be checked at 12 weeks and biweekly thereafter. THE RESEARCHERS RECOMMEND: During periods of illness( in patients receiving Megestrol)…….. Consider EMPIRICAL THERAPY with stress doses of corticosteroids Do not D/C Megace abruptly. Always taper gradually GO BACK TO SLIDE # 66 7 An Interesting Drug-Alcohol Interaction Implications for Drug Abuse 8 An Interesting Drug-Alcohol Interaction **Implications for Drug Abuse** Published in Journal Watch General Medicine January 31, 1992 Citations: DiPadova C et al. Comparison with other H2-receptor antagonists. JAMA 1992 Jan 1 267 83-86 A study measuring the effects of Ranitidine (Zantac®) and Cimetidine (Tagamet®) on the bioavailability of ethanol suggests that drinking with these drugs is NOT a wise choice because………. RANITIDINE AND CIMETIDINE INCREASE BLOOD ALCOHOL LEVELS. 9 An Interesting Drug-Alcohol Interaction **Implications for Drug Abuse** Researchers tested the blood alcohol levels of 20 healthy male volunteers (mean age, 35) During a baseline period and after a oneweek course of EITHER Ranitidine (300 mg/d), Cimetidine (1000 mg/d) or Famotidine (Pepcid) Before each test, the subjects received Oral or intravenous alcohol equivalent to: 1 beer or 1 glass of wine. 10 RESULTS In subjects given alcohol intravenously, none of the three drugs significantly increased alcohol bioavailability. Among subjects taking alcohol ORALLY, bioavailability increased significantly with Ranitidine and Cimetidine ……..but NOT with Famotidine. 11 RESULTS The authors speculate that Ranitidine and Cimetidine affected the absorption of oral doses because they INHIBIT gastric alcohol dehydrogenase activity. However……. Famotidine (Pepcid®) has NO effect on this enzyme! Don’t confuse with Prilosec® (omeprazole which is a PPI and not an H2 Blocker) In patients with regular but moderate alcohol use, Famotidine (Pepcid®) may be a preferable H2- blocker 12 ABUSE POTENTIAL FOR THIS INTERACTION: This study indicates the need for extreme caution when drinking alcohol with Cimetidine or Ranitidine, particularly before driving! As recreational drinking is an ORAL event ………………. This interaction may be intentional in people who want to get inebriated on fewer drinks! 13 Prograf® (tacrolimus): ….Timing is Everything! 14 Prograf® (tacrolimus): INDICATION Tacrolimus is an immunosuppressive agent derived from the fungus Streptomyces tsukubaensis. Originally found in a soil sample taken from the base of Mt. Tsukuba in Japan. Tacrolimus has been studied in patients receiving heart, kidney, liver, lung, pancreas, small bowel, or bone marrow transplants. 15 Prograf® (tacrolimus) Effective in graft rejection prophylaxis and in the management of acute and steroid- or cyclosporine-resistant transplant rejection. Tacrolimus is an alternative to cyclosporine immunosuppression and is10—100 times more potent than cyclosporine 16 Prograf® (tacrolimus) Administer at approximately the same time each day. REASON If given WITH FOOD or WITHIN 1 HOUR OF A MEAL, especially high-fat meals, results in significantly decreased absorption. 17 Goals for Scheduling this drug in relationship to meals Consistency is important TO MINIMIZE ANY Variations in bioavailability. Administer consistently with OR without food. Ask resident what time of day they have been taking this drug at home in relationship to meals times and what type of meal. If possible attempt to accommodate the same schedule. 18