* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Survey
Document related concepts
Real bills doctrine wikipedia , lookup
Nominal rigidity wikipedia , lookup
Edmund Phelps wikipedia , lookup
Fear of floating wikipedia , lookup
Full employment wikipedia , lookup
Interest rate wikipedia , lookup
Post–World War II economic expansion wikipedia , lookup
Long Depression wikipedia , lookup
Austrian business cycle theory wikipedia , lookup
Phillips curve wikipedia , lookup
Monetary policy wikipedia , lookup
Stagflation wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
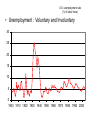
Macroeconomics: Introduction Xu Hu Texas A&M University Outline • Problems macroeconomists are interested in. (Very Brief) • Modeling Concerns (no slide) • Approach for this course(no slide) Important issues in macroeconomics U.S. Real GDP per capita (2000 dollars) • Business Cycles & Industrial Fluctuations 40,000 9/11/2001 First oil price shock 30,000 long-run upward trend… 20,000 Great Depression Second oil price shock 10,000 World War II 0 1900 1910 1920 1930 1940 1950 1960 1970 1980 1990 2000 • Business Cycles & Industrial Fluctuations 1. What are the causes of Boom and Bust? Real Business Cycles theory Excessive Credit Type theory – e.g. Austrian School …… 2. What is the government’s role in the recessions? Fiscal Policy: Tax and Subsidy …… Monetary Policy: Fed cut the interest rate ? …… • Business Cycles & Industrial Fluctuations Fluctuations of the whole economy are sometimes accompanied with “boom and bust “ in the Financial Market Great Depression Recent Crisis Dow Jones Industrial Ave Real GDP 2000 dollars 11,800.0 11,600.0 11,400.0 11,200.0 11,000.0 10,800.0 10,600.0 10,400.0 Real GDP 2000 dollars S&P 500 Unemployment Rate U.S. inflation rate (% per year) • Inflation 25 20 15 Prior to the Great Depression, the inflation rate was fairly low. 10 5 0 -5 -10 -15 1900 1910 1920 1930 1940 1950 1960 1970 1980 1990 2000 • Inflation 1. What do high inflation rates mean to the public?- “The cost of inflation” 2. Inflation and Monetary Policy German Hyperinflation 1919-1923. Germany, 1923: banknotes had lost so much value that they were used as wallpaper. Source: wiki U.S. unemployment rate (% of labor force) • Unemployment : Voluntary and Involuntary 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 1900 1910 1920 1930 1940 1950 1960 1970 1980 1990 2000 Economic Growth 1.What are the factors which influence the speed of economic growth ? 2. How to explain the “gap” between developing countries and developed countries? • Among themselves, macroeconomists often do not have consensuses on certain issues, even some important issues. • Here is an interesting example. Crude Oil prices : Fundamentals V.S. Speculation Debate between two economists • Paul Krugman : The Oil Non-bubble (May 12, 2008) • Guillermo Calvo : Exploding commodity prices, lax monetary policy, and sovereign wealth funds (June 20, 2008) • Paul Krugman: Calvo on Commodities (June 21, 2008)