* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download MS PowerPoint - Catalysis Eprints database
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Woodward–Hoffmann rules wikipedia , lookup
George S. Hammond wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic resolution wikipedia , lookup
Fischer–Tropsch process wikipedia , lookup
Diels–Alder reaction wikipedia , lookup
Hofmann–Löffler reaction wikipedia , lookup
Ene reaction wikipedia , lookup
Vinylcyclopropane rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Stille reaction wikipedia , lookup
Baylis–Hillman reaction wikipedia , lookup
Elias James Corey wikipedia , lookup
Wolff–Kishner reduction wikipedia , lookup
Enantioselective synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
Ring-closing metathesis wikipedia , lookup
Petasis reaction wikipedia , lookup
Strychnine total synthesis wikipedia , lookup
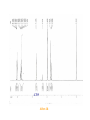
POM catalyzed Synthesis of Methoxy methyl chloride (MOM-Cl) Chloromethyl methyl ether (MOM-Cl) Protection of alcohols, phenols, carboxylic acids, amines, -ketoesters and thiols A one-carbon synthon for alkylation of aromatics and active methylene derivatives Precursors to synthesize methyl ethers and Chloromethyl ether derivatives Halomethylation of aromatic systems Production of MOM-Cl Conventional synthesis of MOM-Cl involves HCHO, HCl and CH3OH Produces the by-product bis[chloromethyl]ether (BCME) BCME is a powerful carcinogen and its use is seriously limited Requires considerable tedious handling during isolation H. Kotsuki, Y. Ushio, N. Yoshimura and M. Ochi, J. Org. Chem. 52 (1987) 2594 D. A. Goff, R. N. Harris, J. C. Bottaro and C. D. Bedford, J. Org. Chem. 51 (1986) 4711 Synthesis of MOM-Cl using POMs as catalysts O O Cl + O O POM O + Cl O 0 60 C Benzoyl chloride (1.0 mol) Dimethoxy methane (1.0 mol) 1.5 g of (0.694 mmol) H3PW12O40 Under N2 atmosphere Reflux at 60 C for 4 h Cool to room temperature Replace the reflux condenser with distillation setup ( 60 C) CMME or MOM-Cl (78 %) 1H NMR was used to follow the conversion with respect to time Integrals of the product MOM-Cl signals ( = 3.52 and 5.46 ppm) were compared with those of dimethoxymethane ( = 3.34 and 4.56 ppm) Conversion of Dimethoxy methane to MOM-Cl followed by 1H NMR The reaction mixture has been analyzed with respect to time by 1H NMR The integrals of the -CH2 signals of the reactant CH3O-CH2-OCH3 and product CH3O-CH2-Cl were compared Trace amount of the reaction mixture has been taken and analyzed by 1H NMR after 1h, 2h and 4h The integrals corresponding to –CH2 signals of the reactant CH3O-CH2-OCH3 resonate at = 4.57 The integrals corresponding to –CH2 signals of the product CH3O-CH2-Cl resonate at = 5.46 were found to increase with respect to time till 4 h. The integrals of –CH2 signals of the product CH3O-CH2-Cl were found to be remained constant after 4 h. So it was concluded that for the maximum conversion the reaction has to be carried out for 4 h. 1H NMR was used to follow the conversion with respect to time Integrals of the product MOM-Cl signals ( = 3.52 and 5.46 ppm) were compared with those of dimethoxymethane ( = 3.34 and 4.56 ppm) MeO- CH2-OMe (--CH2--- 4.57 , --CH3--3.36) 3.852 After 1 h MeO-CH2-Cl ( --CH2---5.46, --CH3—3.51) 4.162 After 2 h 4.709 After 4 h (CH3-O-CH2-Cl) 1H NMR (CDCl3) of isolated MOM-Cl by simple distillation ppm Effect of various POMs in the synthesis of MOM-Cl Entry b c Catalyst Reaction time (h) Yield b (%) TOF c (h−1) 1 H3PW12O40 4 79 26 2 H4SiW12O40 4 66 16 3 H3PMo12O40 4 59 12 4 Cs2.5H0.5PW12O40 4 58 21 5 H2SO4 64 74 2 Isolated yield. TOF: moles of MOM-Cl produced per mol of catalyst per hour The general trend for acid strength among the common heteropolyacids is H3PW12O40 > H4SiW12O40 ≥ H3PMo12O40 I. V. Kozhevnikov, Russ. Chem. Rev. 56 (1987) 811 M. Misono, N. Mizuno, K. Katamura, A. Kasai, Y. Konishi, K. Sakata, T. Okuhara, Y. Yoneda, Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 55 (1982) 400 Features of the process High Bronsted acidity of POMs has been well exploited for the synthesis of valuable reagent MOM-Cl POM function in both heterogeneous and homogeneous Simple distillation to separate the MOM-Cl Maximum yield of the MOM-Cl is 78 % after 4h Absence of carcinogenic byproduct bis[chloromethyl]ether was observed The process can be extended for the synthesis of other R-O-CH2-Cl by suitably employing various other acetals P. S. Kishore, B. Viswanathan, T. K. Varadarajan, Tetrahedron Lett. 47 (2006) 429