* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Electronics
Spark-gap transmitter wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Analog-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Electronics technician (United States Navy) wikipedia , lookup
Radio transmitter design wikipedia , lookup
Josephson voltage standard wikipedia , lookup
Electronic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Transistor–transistor logic wikipedia , lookup
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Printed electronics wikipedia , lookup
Valve audio amplifier technical specification wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Molecular scale electronics wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
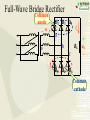
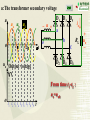
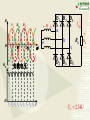
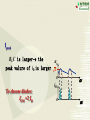
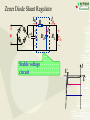
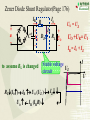
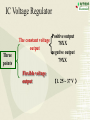
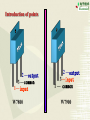
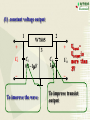
Overview: the Property of Oneway Conduction of diodes Electronics 1. forward bias(P is positive and N is nagative) the current flow is significant 2. reverse bias( P is nagative and N is positive ) the current flow is very small 3. No any one-way conduction when diodes work beyond U BK 4. Reverse current flow will be influnced by temperature. 5.The property of saturation of reverse current flow. Chapter6 Sources of Stable DC Voltage(Page 167) 1. Diode Rectifiers 2. Power Supply Filtering 3. Voltage Regulator Electronics Sources of Stable DC Voltage Electronics The small power supply Transformer Rectifier Regulator Filter Load u1 AC u2 u3 u4 uo DC 1. Diode Rectifiers • Half-Wave Rectifier • Full-Wave Bridge Rectifier Electronics Electronics Half-Wave Rectifier Tr a + u – b D io RL 动画 + uo – u 2U O t uo 2U O ?To calculate the average value of output voltage t U o 0.45U Electronics Full-Wave Bridge Rectifier a + u -– b 4 3 1 2 动画 io u + uo RL – - 2U t uo 2U t Positive half cycle,D1\D3 conduct,D2\D4 are reverse biased ?To calculate the average value of output voltage U o 0.9U Full-Wave Bridge Rectifier Common anode – u + o Electronics D1 D3 D5 io a RL b C + uo – D2 D4 D6 Common cathode u:The transformer secondary voltage u o 2 Electronics D1 D3 D5 u a u b uC 动画 – u + t uo Output voltage io a b o RL C D2 D4 D6 From time t1~t2 : o uo=uab t1 t2 t3 t4 t5 t6 t7 t 8 t9 t + uo – Electronics u o uo o D1 D3 D5 u a u b uC 2 – u + t 负载电压 t1 t2 t3 t4 t5 t6 t7 t 8 t9 t o a b io RL c + uo – D2 D4 D6 U o 2.34U Homework Electronics • To calculate the average value of output voltage in half and full-wave rectifier circuits. • To calculate the average value of current of every diode in half and full-wave rectifier circuits • To calculate the maximum reverse bias voltage that every diode endures in half and full-wave rectifier circuits 2.Power Supply Filtering ~ + u – + C RL C: Smoothing Capacitor + uo – Electronics 2.Power Supply Filtering a + u – b io D i + C ic RL Electronics 动画 u 2U + O uo = u C uo – t 2U O T τ RLC (3 5) 2 (T — the period of voltage) t Electronics Ipeak RLC is larger the uo peak valure of iD is larger 2U O To choose diodes: IOM =2 ID iD O t t 3. Voltage Regulator • Zener Diode Shunt Regulator • Voltage Regulator Electronics Zener Diode Shunt Regulator IR R + u – Electronics IO Iz + + + C UI DZ RL UO – – Stable voltage circuit I UZ U Zener Diode(Page 11) I UZ U Electronics • UZ(2CW13:5~6.5V) • Voltage stable constant (Page 12) Figure 1.3.2 Zener Diode Shunt Regulator(Page 176) IR R + u – IO Iz + + + C UI DZ RL UO – – to assume RL is changed UO = UZ UO +UR= UI IR = I O + I Z Stable voltage UZ circuit RL(IO) IR UO (UZ ) IZ UO IR (IRR) Electronics I U Zener Diode Shunt Regulator(Page 177) there are four parts. T + Ui – + UB – + R3 – + + UZ – R1 R1 +R1 DZUf – R2 + RL UO – reference regular amplifier sample Electronics Electronics T + Ui – output + UB – + UO UB R3 – + + UZ – R1 R1 +R1 DZUf – R1 (1 )U Z R1 R2 R2 + RL UO – Electronics IC Voltage Regulator Three points Positive output The constant voltage 78XX output negative output 79XX Flexible voltage output (1. 25 ~ 37 V ) Electronics Introduction of points 2 —output 3 —common 1—input W7800 2 —output 3—input 1 — common W7900 Electronics (1) constant voltage output 1 + Ui W7805 3 Ci 0.1~1F _ To imorove the wave 2 + CO 1F UO _ UinputUoutputis more than 3V To improve transiet output Electronics (2)Both positive and negative voltage output 1 2 +15V W7815 CO + 3 C 24V i C 1F 1000F 0.33F 220V 24V + C 1000F Ci 1 W7915 CO 0.33F 3 1F 2 – 15V ? • What is significant as a voltage source? Electronics