* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download No Slide Title
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Brushed DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Power over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Solar micro-inverter wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Amtrak's 25 Hz traction power system wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Power supply wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
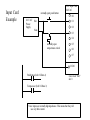
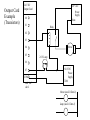
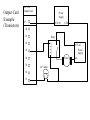
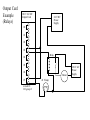
Chapter - PLC Wiring Main Parts of a PLC Power Supply CPU (Central Processing Unit) I/O (Input/Output) Indicator lights PLC Forms Rack Mini Shoebox Micro Software Input Types Proximity Switches Switches Potentiometer LVDTs Voltages 12-24 Vdc 100-120 Vac 10-60 Vdc 12-24 Vac/dc 5 Vdc (TTL) 200-240 Vac 48 Vdc 24 Vac Input Card Example PLC Input Card 24V AC normally open push-button 24 V AC Hot Power Supply Neut. 00 01 02 03 04 normally open temperature switch 05 06 07 COM Pushbutton (bob:3:I.Data.1) it is in rack "bob" slot 3 Te mpsensor (bob:3:I.Data.3) Note: inputs are normally high impedance. This means that they will use very little current. Output Types Solenoid Valves Lights Motor Starters Servo Motors Output Voltages 120 Vac 24 Vdc 12-48 Vac 12-48 Vdc 5Vdc (TTL) 230 Vac Output Card Example (Transistors) 24 V DC Output Card 120 V AC Power Supply Neut. 00 01 Relay 02 03 Motor 04 05 24 V Lamp 06 07 COM rack "sue" slot 2 +24 V DC Power Supply COM Motor (sue:2.O.Data.3) Lamp (sue:2.O.Data.3) Output Card Example (Transistors) 24 V DC Output Card Power Supply V+ +24 V DC COM 00 01 Relay 02 03 04 05 06 07 Motor 24 V lamp 120 V AC Power Supply Neut. Output Card Example (Relays) 120 V AC/DC Output Card 24 V DC Power Supply 00 01 02 03 Relay 04 05 06 Motor 07 in rack 01 I/O group 2 24 V lamp 120 V AC Power Supply Some Design Issues • DC voltages are usually lower, and therefore safer (e.g., 24V). • DC inputs are very fast, AC inputs require a longer on-time. • DC voltages can be connected to more electrical systems. • AC signals are more immune to noise than DC. • AC power is easier and less expensive to supply to equipment. • AC signals are very common. Relays Contactor - Special relays for switching large current loads. Motor Starter - Basically a contactor in series with an overload relay to cut off when too much current is drawn. Arc Suppression - when any relay is opened or closed an arc will jump. This becomes a major problem with large relays. On relays switching AC this problem can be overcome by opening the relay when the voltage goes to zero (while crossing between negative and positive). When switching DC loads this problem can be minimized by blowing pressurized gas across during opening to suppress the arc formation. AC coils - If a normal relay coil is driven by AC power the contacts will vibrate open and close at the frequency of the AC power. This problem is overcome by adding a shading pole to the relay. Problem: You are planning a project that will be controlled by a PLC. Before ordering parts you decide to plan the basic wiring and select appropriate input and output cards. The devices that we will use for inputs are 2 contact switches, a push button and a thermal switch. The output will be for a 24Vdc solenoid valve, a 110Vac light bulb, and a 220Vac 50HP motor. Sketch the basic wiring below including PLC cards. L1 N Wiring Diagram 010 stop start CR1 MCR 020 CR1 030 L1 PLC N 90-1 040 CR1 I:0/0 O:0/0 090 R 050 060 PB1 I:0/1 LS1 I:0/2 100-1 O:0/1 110-1 O:0/2 PB2 070 I:0/3 100 110 120 CR2 ac com 080 CR1 090 90-1 035 100 100-1 050 110 110-1 060 120-1 070 CR2 130 L2 G S1 120-1 O:0/3 120 L1 Drill S tation L1 N JIC Wiring Symbols disconnect (3 phase AC) normally open limit switch normally open push-button circuit interrupter (3 phase AC) normally closed limit switch breaker (3 phase AC) normally closed push-button double pole push-button mushroom head push-button